Renal System
Anatomy/ Kidney Function
Describe main functions of the kidneys
Homeostatic regulation of water and ion content of blood
o Regulation of extra-cellular fluid volume
o Regulation of osmolarity
o Maintenance of [Na+], [K+], [Ca2+], [Cl-] within normal range
o Homeostatic regulation of pH- [H+]/[HCO3-]
Excretion of wastes and foreign substances
o By-product of metabolism-e.g. Creatinine
o Drugs and environmental toxins
Production of hormones
o Not endocrine glands… but can play important roles in endocrine pathways
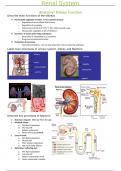
Label main structures of urinary system, kidney and Nephron
Describe key processes of Nephron
1. Bowman’s Capsule- 180L/day filters through
2. Proximal Tubule
a. 70% fluid reabsorbed
b. 54L/ day left
c. Solutes reabsorbed
d. Water follows by osmosis
3. Loop of Henle
a. 90% fluid reabsorbed
b. 18L/day left
c. More solutes reabsorbed
d. Not much water follows
4. Distal loop/ collecting duct
a. 99% fluid reabsorbed
b. 1.5L/day left
c. Solutes reabsorbed if need
d. Water reabsorbed if needed
, Volume and Osmolarity change as fluid flows
through nephron
Summary
1. Kidney regulate ECF vol. and osmolarity- maintains ionic
balance, regulates pH, excretes wastes and foreign substances
and participates in endocrine functions
2. Nephron is functional unit of kidney
3. Nephron carries out FILTRATION, ABSORPTION, SECRETION and EXCRETION
Filtration
What drives filtration?
Force
Filter
Filter
Filtrate has to pass through 3 barriers:
o 1st- Glomerular capillary endothelium
o 2nd – Basal lamina- separates capillary endothelium from
epithelium
o 3rd – Epithelium of Bowmans capsule
Glomerulus is high-pressure filtration system
1. List forces which influence glomerular filtration
Anatomy/ Kidney Function
Describe main functions of the kidneys
Homeostatic regulation of water and ion content of blood
o Regulation of extra-cellular fluid volume
o Regulation of osmolarity
o Maintenance of [Na+], [K+], [Ca2+], [Cl-] within normal range
o Homeostatic regulation of pH- [H+]/[HCO3-]
Excretion of wastes and foreign substances
o By-product of metabolism-e.g. Creatinine
o Drugs and environmental toxins
Production of hormones
o Not endocrine glands… but can play important roles in endocrine pathways
Label main structures of urinary system, kidney and Nephron
Describe key processes of Nephron
1. Bowman’s Capsule- 180L/day filters through
2. Proximal Tubule
a. 70% fluid reabsorbed
b. 54L/ day left
c. Solutes reabsorbed
d. Water follows by osmosis
3. Loop of Henle
a. 90% fluid reabsorbed
b. 18L/day left
c. More solutes reabsorbed
d. Not much water follows
4. Distal loop/ collecting duct
a. 99% fluid reabsorbed
b. 1.5L/day left
c. Solutes reabsorbed if need
d. Water reabsorbed if needed
, Volume and Osmolarity change as fluid flows
through nephron
Summary
1. Kidney regulate ECF vol. and osmolarity- maintains ionic
balance, regulates pH, excretes wastes and foreign substances
and participates in endocrine functions
2. Nephron is functional unit of kidney
3. Nephron carries out FILTRATION, ABSORPTION, SECRETION and EXCRETION
Filtration
What drives filtration?
Force
Filter
Filter
Filtrate has to pass through 3 barriers:
o 1st- Glomerular capillary endothelium
o 2nd – Basal lamina- separates capillary endothelium from
epithelium
o 3rd – Epithelium of Bowmans capsule
Glomerulus is high-pressure filtration system
1. List forces which influence glomerular filtration