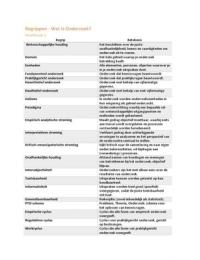
Retail Management by ProfessorBurgerQueen
Retail Pricing Strategies
- EDLP
- retailers price products to offer consumers value at reasonable prices
on a continuous basis. For example, Shoprite promises lowest prices
always, which is in line with their image which reinforces low-price.
- High/Low
- introducing high prices when an item launches and then overtime
discounted and marked down due to the decrease in demand.
- Apple launches new iPhone models every year and introduces these
items at a high price point, and as the hype dies down, these items
are then discounted or price is lowered.
- The benefit of this pricing strategy is that it creates excitement and increases
profit. However, this strategy has the disadvantage of consumers realising
they can wait a few weeks for the items to go on sale.
- Price bundling
- In this pricing strategy the retailers create the impression of extra value.
Retailers offer more than one item for a set price or a set of different
items for a single price. For example, Clicks often runs the buy three items
for the price of two promotions.
- Odd pricing
- Retailers use this strategy to make customers feel as though they are
paying less than they actually are. Retailers use odd numbers for the last
digits of the price, which from a psychological perspective makes the
merchandise appear cheaper. For example, R14.99 instead of R15.00.
Retail Pricing Strategies
- EDLP
- retailers price products to offer consumers value at reasonable prices
on a continuous basis. For example, Shoprite promises lowest prices
always, which is in line with their image which reinforces low-price.
- High/Low
- introducing high prices when an item launches and then overtime
discounted and marked down due to the decrease in demand.
- Apple launches new iPhone models every year and introduces these
items at a high price point, and as the hype dies down, these items
are then discounted or price is lowered.
- The benefit of this pricing strategy is that it creates excitement and increases
profit. However, this strategy has the disadvantage of consumers realising
they can wait a few weeks for the items to go on sale.
- Price bundling
- In this pricing strategy the retailers create the impression of extra value.
Retailers offer more than one item for a set price or a set of different
items for a single price. For example, Clicks often runs the buy three items
for the price of two promotions.
- Odd pricing
- Retailers use this strategy to make customers feel as though they are
paying less than they actually are. Retailers use odd numbers for the last
digits of the price, which from a psychological perspective makes the
merchandise appear cheaper. For example, R14.99 instead of R15.00.