Pneumonia
lung parenchyma inflammation due to lower respiratory tract infection,
leading to puss-filled alveoliand
consolidation.
in
Can result perfusion (hypoxial,
reduced
·
as well as restricted ventilation from pain/effusion (T2RF).
Can lead to effusion, lung abcess, and Pericarditis.
·
Types:
·
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP): develops outside of hospital.
-
most
commonly caused by strep, followed by viral.
·
Hospital- Acquired Pneumonia (HAP):develops more than 48h after hospital admission.
ventilator associated Pneumonia develops after intubation.
· -
-
·
Guidelines based on VAP causes, which are
completely differentto CAP.
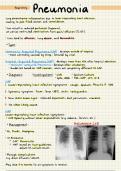
·Diagnosis:·Investigations: CXR Sputum Culture
- -
SqOz, ABG-FBC, CRP, LFT, UTE
-
CAP:
infection
1.Lower
respiratory tract
symptoms:cough, sputum, Pleuritic 9, SOB.
2. Systemic symptom:fever, Temp 38°C, chills, tachycardia.
3. New chestexam
signs:reduced expansion, dull percussion, crackles.
4. No other
likely cause.
HAP:
Lower
respiratory tractinfection symptoms
+
(XROpacity without other explanation (e.g. oedema, fibrosis, etc.)
PNEUMONIA CXR
·
Management:
Oz, Fluids, Analgesia.
·
IV Antibiotics
·
CAP:Amoxicillin
HAP:based on
guidelines,
trust
adjust on culture results.
Manage complications
·
e.g. drain effusion/abcess.
May take 3-6 months for all symptoms to resolve.