• Mechanisms by which glomerular ltrate is altered to produce urine
• Reabsorption from and secretion into the glomerular ltrate within the tubule
• Active and passive transport in the renal tubule
• Techniques to investigate renal active and passive transport
• The structural components of tubule & the function of each segment
• Counter-current exchange and the Loop of Henle
• Abnormalities of urine and kidneys
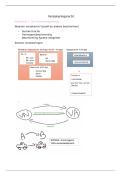
modi cation of ultra ltrate
glomerular ltrate
• ltrate that is produced after ltration of the glomerular apparatus
• GF = same composition as PLASM
◦ NO CELLS - little protein (small that can pass glomerulus)
• composition of URINE di erent to plasma
• how does this happen???
◦ GF formed at 120ml/min ( ow rate)
◦ urine ow = 1ml/min (slower)
how is the ltrate selectively modi ed as it passes through the tubule to turn the ltrate into
urine?
• blood supply continues to say close to tubule = TUBULAR CAPILLARIES
◦ exchange of components (glomerular ltrate + plasma)
• process of reabsorption - taken across epithelial --> capillary
• molecules go from PLASMA --> FLUID (SECRETION - movement of molecules in the opposite
direction)
reabsorption and secretion
• tubule has epithelial cells either side
• glomerular tubule runs top --> bottom
towards excretion
• REABSORPTION - transfer of materials
from TUBULAR LUMEN (across e cells)
--> PERITUBULAR PLASMA
• SECRETION - transfer of materials from
PERITUBULAR PLASMA --> TUBULAR
LUMEN
◦ happens via ACTIVE TRANSPORT;
PASSIVE FLUX; CO-TRANSPORT
transport in tubule
• COMBINATION of active + passive mechanisms
◦ transport is TRANSCELLULAR - passes e cells + goes across both luminal + basolateral
membranes of e cells in either direction
• GLUT2 glucose transporter
• familial renal glycosuria - condt where SGLT2 transporter is MISSING - unable to taken glucose
fi
fi
, OUT OF GLOMERULAR ltrate --> urinate glucose = glyco-urea
• - SGLT2 inhibitors used to TREAT diabetes - DAPAGLIFLOZIN - block transporter and secrete
more urine to decrease glucose levels in the blood
• Techniques to investigate renal active and passive transport
techniques to investigate tubular function
• CLEARANCE STUDIES - appleid to man (observational)
• MICRO-PUNCTURE + ISOLATED PERFUSED TUBULE - applied to lab animals (mechanistic)
• ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL ANALYSIS - applied to lab animals - mechanistic)
◦ potential measurement
◦ patch clamping
micro-puncture
• tubule is punctured with a micro-pipette
• that puncture used to inject viscous oil
• second injection with uid we want to study (composition of
study is KNOWN)
• the VISCOUS OIL HELPS with preventing of mixing of uid +
glomerular ltrate coming in or backward di usion
• after a period time - REMOVE LIQUID + ANALYSE
COMPOSITION --> see how tubule modi ed solution
electrophysiology - electrical potential
• use micro-electrode to measure potential across a membrane
• combine with MICRO-PERFUSION to alter potential di erence
• measure whether ION MOVING WITH/ AGAINST electrochemical gradient
◦ actively transported?
electrophysiology - patch clamping
• ion ow can be measured through single channel -
measure electrical resistance
◦ across patch of cell membrane
◦ changes when channels open/ close
• types of channels + response to drugs +
hormones that will a ect transporters
clearance studies
• measurement of volume of plasma that is removed
over period of time - RENAL CLEARANCE
fi