A market is any arrangement that enables buyers and sellers to get information
and to do business with each other.
- A competitive market is a market that has many buyers and many
sellers so no single buyer or seller can influence the price
What determines market structure:
- Number of firms in the market
1. Concentration ratio
- Barriers to entry and exit
1. Natural barriers: one firm supplying the whole market at the
lowest cost
2. Ownership
3. Legal barriers
- Firm’s control over prices
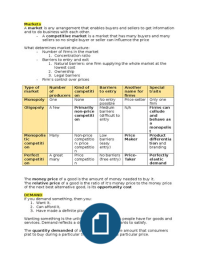
Type of Number Kind of Barriers Another Special
market of competiti to entry name for traits
producers on firms
Monopoly One None No entry Price-setter Only one
possible firm
Oligopoly A few Primarily Medium N/A Firms can
non-price barriers collude
competiti (difficult to and
on entry behave as
a
monopolis
t
Monopolis Many Non-price Low Price Product
tic competitio barriers Maker differentia
competiti n: price (easy tion and
on competitio entry) branding
n
Perfect A great Price No barriers Price- Perfectly
competiti many competitio (free entry) Taker elastic
on n demand
The money price of a good is the amount of money needed to buy it.
The relative price of a good is the ratio of it’s money price to the money price
of the next best alternative good, is its opportunity cost
DEMAND
If you demand something, then you:
1. Want it,
2. Can afford it,
3. Have made a definite plan to buy it
Wanting something is the unlimited desire or wishes people have for goods and
services. Demand reflects a decision about which wants to satisfy.
The quantity demanded of a good or service is the amount that consumers
plat to buy during a particular time period and at a particular price.
,The law of demand states: other things remaining the same, the higher the
price of a good, the smaller is the quantity demanded, or the lower the price of a
good, the larger is the quantity demanded.
- Substitution effect
- Income effect
Substitution effect:
When the relative price (opportunity cost) of a good or service rises, people seek
substitutes for it, so the quantity demand of the good or service will decrease.
A rise in the price and no other factor changing brings a decrease in the quantity
demanded and a movement up along the demand curve.
Six main factors that change demand:
1. The price of related goods
1. A substitute is a good that can be used in place of another
good. (yoghurt/milk)
2. A complement is a good that is used in conjunction with
another good. (duster, duster bags)
2. Expected future prices
1. If the price of the good changes and other things remain the
same, the quantity demanded changes and there is a movement
along the demand curve
2. Price increase -> demand decreases
3. Price decrease -> demand increases
3. Income
1. When income increase, consumers buy more of most goods and
the demand curve shifts rightward.
4. Expected future income and credit
1. People tend to act upon their expectations. whiter they will
happen or not.
5. Population
1. The larger the population, the greater is the demand for all
goods.
6. Preferences
1. People with the same income have different demands if they
have different preferences.
When some influence on buying plans other than the price of the good changes,
there is a change in demand for that good.
the quantity of the good that people plan to buy changes at each and every
price, so there is a new demand curve.
- When demand increase, the demand curve shifts rightward
- When demand decreases, the demand curve shifts leftward
- A normal good is one for which demand increases as the income
increases.
, - An inferior good is a good for which demand decreases as income
increases.
Decrease in demand the curve shifts to the left and if there is an increase in
demand the demand curve will shift to the right.
Demand increase -> curve rightward
Demand decrease -> curve leftward
SUPPLY
Resources and technology determine what a firm I possible to produce. Supply
reflects a decision about which technologically feasible items to produce.
The quantity supplied of a good or service is the amount that producers plan
to sell during a given time period at a particular price
The law of supply states, the higher the price of a good, the greater is the
quantity supplied. If the price of good lowers, the smaller is the quantity
supplied.
Producers are willing to supply a good only if they can at least cover their
(marginal) cost of production
The production process uses the following factors of production:
1. Land – natural resources
2. Labour – human resources
3. Capital – man made resources
4. Entrepreneurship – the human resources that organizes land, labour and
capital (management)
- Land = rent
- Labour = wages
- Capital = interest
- Entrepreneurship = profit
Profit maximization: if costs are constant and prices per unit are rising, the
opportunity of increasing profit leads to an increase in production
When some influence on selling plans other than the price of the good changes,
there is a change in supply of that good.
The quantity of the good that producers plan to sell changes at each and every
price, so there is a new supply curve.
When supply increases, the supply curve shifts rightward. When supply
decreases, the supply curve shifts leftward.
Supply increase -> curve rightwards
Supply decrease -> curve leftwards
The six main factors that change supply of a good:
1. The prices of factors of production
If the price of a factor of production used to produces a good rises, the
costs to produce are higher. Which will result in the supplier is no
longer willing to produce the same quantity.
So a rise in the price of a factor of production decreases supply and
shifts the supply curve leftward.