1.11.19
L5 – Thyroid (bow tie)
Keywords:
Auscultation (listening to sounds of the heart/lungs/other organs w/stethoscope),malignant (vicious
cancer)
Lecture:
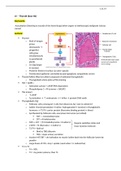
Thyroid
o Back of tongue
grows
downwards →
progenitor (Colloid)
cells grow
simultaneously
to parathyroid W/fenestrated caps, lymph
glands vessels and sympathetic
nerve endings
o 10-20g (larger
in women)
o Posterior binds to trachea via outer capsule
o Fenestrated capillaries controlled by post-ganglionic sympathetic nerves
Thyroid follicle filled w/colloid composed of iodinated thyroglobulin
o Thyroglobulin stains pink w/PAS staining
TSH + GCPR =
o Adenylate cyclase = cAMP/PKA-dependent
o Phospholipase C = PI turnover = DAGIP3
TSH impact
o ↑cAMP
o Tg ionization → ↑ endocytosis → I- influx → protein/DNA synth
Thyroglobulin (Tg)
o Follicular cells cotransport I- cells from blood via Na+ next to colloid AT
o Iodide -thyroid peroxidase→ Iodine -hydrogenated→ tyrosine in thyroglobulin
hormone → T3/T4 -carrier protein (thyroxine binding protein)→ blood
o Synthesized by follicular cells, exocytose into lumen (w/colloid)
MIT = monoiodotyrosine
DIT = di-iodotryosine
o MITs + DIT = (T3 triiodothyronine =3 iodine’s) Require oxidative states and
o 2 DITS = T4 (thyroxine = 4 iodine’s) loses tyrosine molecule
o T3/T4 = lipid sol
Bind to TBG/albumin
TBG = stops urinary secretion
o Inactive MIT/DIT = de-iodination to recycle iodine back into the follicular lumen by
pendrin
o Large doses of ClO4- stop I- uptake (used when I- is radioactive)
T4 vs T3
o T4 = 90%
o T3 = 4x greater potency than T4
, 1.11.19
o Liver and kidney can dehydrogenase T4 into T3
o Bind to intracellular receptors (bc lipid soluble)
Receptor = hormone-responsive TF (w/binding site for DNA to alter)
T3 ↑ potency bc ↑ affinity = ↑ stable
Effects of thyroid hormone
o ↑ BMR (↑o2 consumption and heat)
o ↑ CV (↑HR, CO, force of contraction)
Bc ↑ breathing
o NS (↑ catecholamine effect and to sympathetic NS)
o Growth/maturation (embryos, CNS and linear GH growth)
Goitre = excessively large thyroids (under or overactive thyroid)
o Excessive TSH
o Usually w/autoimmune disease
o Hypothyroidism
Symptoms in adult (weight gain, cold intolerant, lethargic, depression, puffy
skin, myxedema, sluggish reflexes, muscle weakness, ↓HR/CO)
Pendred syndrome = caused by pendrin gene mut
Symptoms in child (Cretinism – permanent brain damage, shortness, obesity
an
Heal prick test – measure TSH, if ↑ = ↓ - feedback w/T3/4)
Thyroid replacement therapy
Iodine deficiency disorder (IDD) < 50ug/day
↑ proportion of T3:T4 = ↑ TSH
↑ cause of brain damage, diplegia and deafness in infants
Symptoms: sometimes no goiter, fatigue and ↓ intelligence (15 IQ
point loss)
Treatment
T4 replacement therapy (150ug/day)
If goiter bc IDD then ↑ dietary iodine
Causes
Primary failure (↓T3/4 = ↑TSH)
Secondary failure (↓TRH/TSH bc hypothalamus/pit mut = np goiter)
Secondary failure (autoimmune (hashumotos thyroididisis = ↓T3/4
= ↑TSH = goiter)
Secondary failure lack of dietary iodine (↓T3/4 = ↑TSH
o Hyperthyroidism
Symptoms (weight loss, nervousness, heat intolerant, ↑HR/CO, tremors,
hair loss and high fatigue )
Graves’ disease (50% of all cases) autoimmune
Anti-Tg/anti-TPO antibodies bind to TSH receptors to mimic and not
regulated by – feedback = (↑T3/4 = ↓TSH = goiter)
Graves orbitopathy – eye inflammation → puffy upper lid, eye bags,
watery eyes and exophthalmos
o After binding TSI to thyrotropin receptors in retro-orbital
tissues (eye proboscis (moving forward) releases pressure)
o Cause of thyrotoxicosis
o Tape eyelids closed at night
L5 – Thyroid (bow tie)
Keywords:
Auscultation (listening to sounds of the heart/lungs/other organs w/stethoscope),malignant (vicious
cancer)
Lecture:
Thyroid
o Back of tongue
grows
downwards →
progenitor (Colloid)
cells grow
simultaneously
to parathyroid W/fenestrated caps, lymph
glands vessels and sympathetic
nerve endings
o 10-20g (larger
in women)
o Posterior binds to trachea via outer capsule
o Fenestrated capillaries controlled by post-ganglionic sympathetic nerves
Thyroid follicle filled w/colloid composed of iodinated thyroglobulin
o Thyroglobulin stains pink w/PAS staining
TSH + GCPR =
o Adenylate cyclase = cAMP/PKA-dependent
o Phospholipase C = PI turnover = DAGIP3
TSH impact
o ↑cAMP
o Tg ionization → ↑ endocytosis → I- influx → protein/DNA synth
Thyroglobulin (Tg)
o Follicular cells cotransport I- cells from blood via Na+ next to colloid AT
o Iodide -thyroid peroxidase→ Iodine -hydrogenated→ tyrosine in thyroglobulin
hormone → T3/T4 -carrier protein (thyroxine binding protein)→ blood
o Synthesized by follicular cells, exocytose into lumen (w/colloid)
MIT = monoiodotyrosine
DIT = di-iodotryosine
o MITs + DIT = (T3 triiodothyronine =3 iodine’s) Require oxidative states and
o 2 DITS = T4 (thyroxine = 4 iodine’s) loses tyrosine molecule
o T3/T4 = lipid sol
Bind to TBG/albumin
TBG = stops urinary secretion
o Inactive MIT/DIT = de-iodination to recycle iodine back into the follicular lumen by
pendrin
o Large doses of ClO4- stop I- uptake (used when I- is radioactive)
T4 vs T3
o T4 = 90%
o T3 = 4x greater potency than T4
, 1.11.19
o Liver and kidney can dehydrogenase T4 into T3
o Bind to intracellular receptors (bc lipid soluble)
Receptor = hormone-responsive TF (w/binding site for DNA to alter)
T3 ↑ potency bc ↑ affinity = ↑ stable
Effects of thyroid hormone
o ↑ BMR (↑o2 consumption and heat)
o ↑ CV (↑HR, CO, force of contraction)
Bc ↑ breathing
o NS (↑ catecholamine effect and to sympathetic NS)
o Growth/maturation (embryos, CNS and linear GH growth)
Goitre = excessively large thyroids (under or overactive thyroid)
o Excessive TSH
o Usually w/autoimmune disease
o Hypothyroidism
Symptoms in adult (weight gain, cold intolerant, lethargic, depression, puffy
skin, myxedema, sluggish reflexes, muscle weakness, ↓HR/CO)
Pendred syndrome = caused by pendrin gene mut
Symptoms in child (Cretinism – permanent brain damage, shortness, obesity
an
Heal prick test – measure TSH, if ↑ = ↓ - feedback w/T3/4)
Thyroid replacement therapy
Iodine deficiency disorder (IDD) < 50ug/day
↑ proportion of T3:T4 = ↑ TSH
↑ cause of brain damage, diplegia and deafness in infants
Symptoms: sometimes no goiter, fatigue and ↓ intelligence (15 IQ
point loss)
Treatment
T4 replacement therapy (150ug/day)
If goiter bc IDD then ↑ dietary iodine
Causes
Primary failure (↓T3/4 = ↑TSH)
Secondary failure (↓TRH/TSH bc hypothalamus/pit mut = np goiter)
Secondary failure (autoimmune (hashumotos thyroididisis = ↓T3/4
= ↑TSH = goiter)
Secondary failure lack of dietary iodine (↓T3/4 = ↑TSH
o Hyperthyroidism
Symptoms (weight loss, nervousness, heat intolerant, ↑HR/CO, tremors,
hair loss and high fatigue )
Graves’ disease (50% of all cases) autoimmune
Anti-Tg/anti-TPO antibodies bind to TSH receptors to mimic and not
regulated by – feedback = (↑T3/4 = ↓TSH = goiter)
Graves orbitopathy – eye inflammation → puffy upper lid, eye bags,
watery eyes and exophthalmos
o After binding TSI to thyrotropin receptors in retro-orbital
tissues (eye proboscis (moving forward) releases pressure)
o Cause of thyrotoxicosis
o Tape eyelids closed at night