The Abducens Nerve (CN VI)
The abducens nerve contains only somatic motor neurones, so has no
sensory function
Anatomical course:
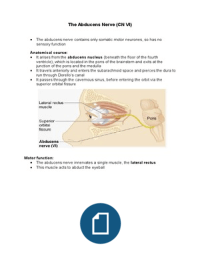
It arises from the abducens nucleus (beneath the floor of the fourth
ventricle), which is located in the pons of the brainstem and exits at the
junction of the pons and the medulla
It travels anteriorly and enters the subarachnoid space and pierces the dura to
run through Dorello’s canal
It passes through the cavernous sinus, before entering the orbit via the
superior orbital fissure
Motor function:
The abducens nerve innervates a single muscle, the lateral rectus
This muscle acts to abduct the eyeball
The abducens nerve contains only somatic motor neurones, so has no
sensory function
Anatomical course:
It arises from the abducens nucleus (beneath the floor of the fourth
ventricle), which is located in the pons of the brainstem and exits at the
junction of the pons and the medulla
It travels anteriorly and enters the subarachnoid space and pierces the dura to
run through Dorello’s canal
It passes through the cavernous sinus, before entering the orbit via the
superior orbital fissure
Motor function:
The abducens nerve innervates a single muscle, the lateral rectus
This muscle acts to abduct the eyeball