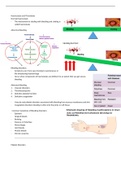
Haemostasis I - Platelets and primary haemostasis Haemopoiesis:
Megakaryopoiesis:
- Myeloid lineage
- Thrombopoiesis (TPO) is a growth factor
- Synthesised by liver
- TPO is involved in all stages of
megakaryopoiesis and thrombopoiesis
- Largest (50 - 100um) and rarest cells in BM
- Polyploid
- Unique to mammals
- Can produce around 3000 platelets, compared to 2 daughter cells in other lineages
- Platelet formation is far more complicated than the production of white cells
Platelet Production - Thrombopoiesis
1. Phase I - Megakaryocyte maturation
a. Endomitosis (DNA replication with cell division)
b. Cytoplasm enlargement (cytoskeletal proteins and platelet granules)
2. Phase II - Platelet generation
a. Mature megakaryocytes extend long branching processes (proplatelets)
b. Organelles and granules are transported to proplatelets
c. Driven by cytoskeletal rearrangements
, Platelets:
- Anuclear (no nucleus)
- 1-3um in diameter
- Normal = 150 - 400 x 10^9/L
- Higher than normal = thrombocytosis
- Lower than normal = thrombocytopenia
- Platelets circulate for 7-10 days
- Each day, 100 billion platelets must be produced from megakaryocytes
(MKs) to maintain the normal platelet count
Platelet structure:
- Disc shaped
- No nucleus
- Plenty of them
- Small 1-3um
Platelet structure - granules
- Platelets can’t synthesis as they don’t have a nucleus
- Granules allow storage of molecules that the platelets need to perform their function
- Platelets contain 3 types of storage granule:
Megakaryopoiesis:
- Myeloid lineage
- Thrombopoiesis (TPO) is a growth factor
- Synthesised by liver
- TPO is involved in all stages of
megakaryopoiesis and thrombopoiesis
- Largest (50 - 100um) and rarest cells in BM
- Polyploid
- Unique to mammals
- Can produce around 3000 platelets, compared to 2 daughter cells in other lineages
- Platelet formation is far more complicated than the production of white cells
Platelet Production - Thrombopoiesis
1. Phase I - Megakaryocyte maturation
a. Endomitosis (DNA replication with cell division)
b. Cytoplasm enlargement (cytoskeletal proteins and platelet granules)
2. Phase II - Platelet generation
a. Mature megakaryocytes extend long branching processes (proplatelets)
b. Organelles and granules are transported to proplatelets
c. Driven by cytoskeletal rearrangements
, Platelets:
- Anuclear (no nucleus)
- 1-3um in diameter
- Normal = 150 - 400 x 10^9/L
- Higher than normal = thrombocytosis
- Lower than normal = thrombocytopenia
- Platelets circulate for 7-10 days
- Each day, 100 billion platelets must be produced from megakaryocytes
(MKs) to maintain the normal platelet count
Platelet structure:
- Disc shaped
- No nucleus
- Plenty of them
- Small 1-3um
Platelet structure - granules
- Platelets can’t synthesis as they don’t have a nucleus
- Granules allow storage of molecules that the platelets need to perform their function
- Platelets contain 3 types of storage granule: