Physiology notes
Hypothalamus: regulates body temperature, fluid balance, and energy
balance
3 components of neuronal response:
1. Humoral response
2. Visceromotor response
3. Somatic motor response
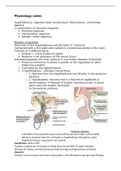
Pituitary (hypofyse)
Extension of the hypothalamus and the brain 3rd ventricle.
Connected with a thin stalk and cradled in a protective pocket of the skull.
Consists of 2 different parts:
Anterior = a true endocrine gland
Posterior = an extension of the neural tissue
Activates/regulates the slow systems in your body (releases hormones)
Produces hormones involved in growth or the regulation of other
endocrine systems
Controlled by the hypothalamus
2 hypothalamus – pituitary connections:
o 1. Neurons from the hypothalamus end directly in the posterior
pituitary
o 2. hypothalamic neurons end in a first set of capillaries (a
portal system) Release of trophic neurohormones portal
veins carry the trophic hormones
to the anterior pituitary.
Posterior pituitary
- Cell bodies in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and supra-optic nucleus (SON)
- Hormone transport from the cell bodies in hypothalamus through the axons.
- Peptide hormones: vasopressin and oxytocin
Vasopressin: ADH or AVP
Function: vasopressin increase in blood pressure and ADH water retention
Stimulus for release: low blood pressure/haemorrhage and high plasma osmolarity
Oxytocin:
Function: uterus muscle contraction during labour and milk ejection during breast-feeding.
Hypothalamus: regulates body temperature, fluid balance, and energy
balance
3 components of neuronal response:
1. Humoral response
2. Visceromotor response
3. Somatic motor response
Pituitary (hypofyse)
Extension of the hypothalamus and the brain 3rd ventricle.
Connected with a thin stalk and cradled in a protective pocket of the skull.
Consists of 2 different parts:
Anterior = a true endocrine gland
Posterior = an extension of the neural tissue
Activates/regulates the slow systems in your body (releases hormones)
Produces hormones involved in growth or the regulation of other
endocrine systems
Controlled by the hypothalamus
2 hypothalamus – pituitary connections:
o 1. Neurons from the hypothalamus end directly in the posterior
pituitary
o 2. hypothalamic neurons end in a first set of capillaries (a
portal system) Release of trophic neurohormones portal
veins carry the trophic hormones
to the anterior pituitary.
Posterior pituitary
- Cell bodies in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and supra-optic nucleus (SON)
- Hormone transport from the cell bodies in hypothalamus through the axons.
- Peptide hormones: vasopressin and oxytocin
Vasopressin: ADH or AVP
Function: vasopressin increase in blood pressure and ADH water retention
Stimulus for release: low blood pressure/haemorrhage and high plasma osmolarity
Oxytocin:
Function: uterus muscle contraction during labour and milk ejection during breast-feeding.