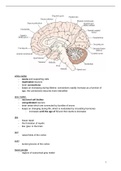
white matter
- axons and supporting cells
- myelinated neurons
- brain connections
- keeps on increasing during lifetime: connections rapidly increase as a function of
age, the connections become more intensified
gray matter
- neuronal cell bodies
- unmyelinated neurons
- brain areas which are connected by bundles of axons
- keeps on changing during life, which is modulated by circulating hormones
- increases until the age of 12 and then starts to decrease
glia
- tissue repair
- the formation of myelin
- like ‘glue’ in the brain
gyri
- raised folds of the cortex
sulci
- buried grooves of the cortex
basal ganglia
- regions of subcortical gray matter
1
, - consist of caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus
- motor control and skill learning
diencephalon
- subcortical gray matter
- including the thalamus and hypothalamus
thalamus
- major subcortical relay center
- processing station between all sensory organs (except smell) and the cortex
hypothalamus
- small structure in the middle of the brain
- variety of nuclei
- medial preoptic area (MPOA)
- directly connected to and controlling the pituitary gland
- different functions
- emotions
- hypothalamus → pituitary gland → peptide → emotion
- coordinates the ANS directly
- can affect bodily responses, neuropeptide system and steroid hormonal
system
- produces steroid hormones
pituitary gland
- secretes many different hormones
- produces neuropeptides (opioids/ endorphins, vasopressin and oxytocin)
insula/ insular cortex
- a region of cortex lying beneath the temporal lobes
- part of the emotional brain
- main node of the salience network which activates in response to any relevant
stimulus (threat, reward, etc)
- monitors bodily perception and feelings (arousal) in general
- involved in
- subjective experience of any emotion
- interoceptive awareness: arousal
- emotions: disgusts (seeing disgust expressions, feeling disgusted and moral
disgust) and other emotions
- taste and pain perception
- social aversion network
- cognitive and affective empathy
- body awareness of emotional body language (EBL)
- lesion impairs disgust recognition in faces and sometimes voices
anterior insula (AI)
- involved in regular smelling (not social smells)
- codes effect of property of smell (“do we want to approach or avoid?”
2
, subcortex/ reptilian brain
- midbrain/ brainstem
- small nuclei with distinct (non-)social roles
- contains limbic system: amygdala and insula
- action-reaction: fight-flight mechanism
limbic system/ mammalian brain
- region of subcortex
- consists of
- hypothalamus: control of ANS and
hormones
- amygdala: fear and other emotions
- hippocampus: mainly (emotional) memory
- insula: disgust and other emotions
- striatum: reward and joy
- cingulate cortex
- mammillary bodies
- involved in relating the organism to the environment
- emotionality: behavior flexibility
- specific for fear and disgust
- behavior based on attention and conditioning
neocortex/ primate brain
- no separate brain areas
- rationality: behavioral control
- exception: mirror neurons might have specific social function
- behavior based on subjective/ affective experience: feel and explain how we feel,
social interaction and rational thinking
cortex
- 2 cortical parts
- orbitofrontal cortex (OFC)
- anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
- both part of the neocortex (some say ACC is part of the limbic system)
- motivation/ reward
- needs time to fully develop
anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
- part of the emotional brain
- monitoring responses
- automatic conflict-detection system
- experience of emotion
- important for conflict monitoring (both self and observed conflicts)
- if you have learned that a certain stimulus is associated with a reward and
this association is violated or reversed, then you need the anterior cingulate
cortex to adjust your behavior
- use dorsal and ventral part to adjust behavior
3
- axons and supporting cells
- myelinated neurons
- brain connections
- keeps on increasing during lifetime: connections rapidly increase as a function of
age, the connections become more intensified
gray matter
- neuronal cell bodies
- unmyelinated neurons
- brain areas which are connected by bundles of axons
- keeps on changing during life, which is modulated by circulating hormones
- increases until the age of 12 and then starts to decrease
glia
- tissue repair
- the formation of myelin
- like ‘glue’ in the brain
gyri
- raised folds of the cortex
sulci
- buried grooves of the cortex
basal ganglia
- regions of subcortical gray matter
1
, - consist of caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus
- motor control and skill learning
diencephalon
- subcortical gray matter
- including the thalamus and hypothalamus
thalamus
- major subcortical relay center
- processing station between all sensory organs (except smell) and the cortex
hypothalamus
- small structure in the middle of the brain
- variety of nuclei
- medial preoptic area (MPOA)
- directly connected to and controlling the pituitary gland
- different functions
- emotions
- hypothalamus → pituitary gland → peptide → emotion
- coordinates the ANS directly
- can affect bodily responses, neuropeptide system and steroid hormonal
system
- produces steroid hormones
pituitary gland
- secretes many different hormones
- produces neuropeptides (opioids/ endorphins, vasopressin and oxytocin)
insula/ insular cortex
- a region of cortex lying beneath the temporal lobes
- part of the emotional brain
- main node of the salience network which activates in response to any relevant
stimulus (threat, reward, etc)
- monitors bodily perception and feelings (arousal) in general
- involved in
- subjective experience of any emotion
- interoceptive awareness: arousal
- emotions: disgusts (seeing disgust expressions, feeling disgusted and moral
disgust) and other emotions
- taste and pain perception
- social aversion network
- cognitive and affective empathy
- body awareness of emotional body language (EBL)
- lesion impairs disgust recognition in faces and sometimes voices
anterior insula (AI)
- involved in regular smelling (not social smells)
- codes effect of property of smell (“do we want to approach or avoid?”
2
, subcortex/ reptilian brain
- midbrain/ brainstem
- small nuclei with distinct (non-)social roles
- contains limbic system: amygdala and insula
- action-reaction: fight-flight mechanism
limbic system/ mammalian brain
- region of subcortex
- consists of
- hypothalamus: control of ANS and
hormones
- amygdala: fear and other emotions
- hippocampus: mainly (emotional) memory
- insula: disgust and other emotions
- striatum: reward and joy
- cingulate cortex
- mammillary bodies
- involved in relating the organism to the environment
- emotionality: behavior flexibility
- specific for fear and disgust
- behavior based on attention and conditioning
neocortex/ primate brain
- no separate brain areas
- rationality: behavioral control
- exception: mirror neurons might have specific social function
- behavior based on subjective/ affective experience: feel and explain how we feel,
social interaction and rational thinking
cortex
- 2 cortical parts
- orbitofrontal cortex (OFC)
- anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
- both part of the neocortex (some say ACC is part of the limbic system)
- motivation/ reward
- needs time to fully develop
anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
- part of the emotional brain
- monitoring responses
- automatic conflict-detection system
- experience of emotion
- important for conflict monitoring (both self and observed conflicts)
- if you have learned that a certain stimulus is associated with a reward and
this association is violated or reversed, then you need the anterior cingulate
cortex to adjust your behavior
- use dorsal and ventral part to adjust behavior
3