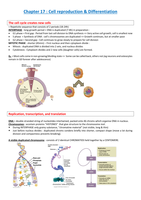
The cell cycle creates new cells
= Repetivite sequence that consists of 2 periods (18-24h)
INTERPHASE : long-growth period + DNA is duplicated (7-8h) in preparation :
G1 phase = First gap : Period from last cell division to DNA synthesis => Very active cell growth, cell is smallest now
S phase = Synthesis of DNA : cell’s chromosomes are duplicated => Growth continues, but at smaller pace
G2 phase = Second gap : Cell continues to grow slowly to prepare for cell division
MITOTIC PHASE : shorter (45min) – First nucleus and then cytoplasm divide :
Mitosis : duplicated DNA is divided into 2 sets, and nucleus divides
Cytokinesis : Cytoplasm divides and 2 new cells (daughter cells) are formed.
G0 = Most cells come in non-growing/dividing state => Some can be called back, others not.(eg neurons and osteocytes
remain in G0 forever after adolescence)
Replication, transcription, and translation
DNA = double-stranded string of nucleotides intertwined, packed onto 46 chroms which organise DNA in nucleus.
Chromosomes : acontain proteins “HISTONES” that give structure to the chromosome mol.
During INTERPHASE only grainy substance, “chromatine material” (not visible, long & thin)
Just before nucleus divides : duplicated chroms condens briefly into shorter, compact shape (move a lot during
division and compactness prevents breaking).
A visible duplicated chromosome : consists of 2 identical CHROMATIDS held together by a CENTOMERE.