CORRECT ANSWERS |\
1. What are the three fundamental questions every economy
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
must answer? |\
Give an example of a "What" question. 1. What to produce? Ex:
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
One business wants to drill for oil, the other want to raise cattle.
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
2. How to produce it? Ex: Company needs to decide to use a
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
current factory or find a new location. 3. From who to produce?
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
10 Principles of economics?
|\ |\ |\
1. People face trade-offs
|\ |\ |\
2. The cost of something is what you give up to get it
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
3. Rational people think at the margin
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
4. People respond to incentives
|\ |\ |\ |\
5. Trade can make everyone better off
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
6. Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
7. Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
8. A country's standard of living depends on its ability to produce
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
goods and services
|\ |\ |\
9. Prices rise when the government prints too much money
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
10. Society faces a short-run trade-off between inflation and
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
unemployment
,11. Identify the payment that goes to each of the four factors of
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
production?
1. Natural resources: rent for land and buildings. 2. Labor: wages
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
3.Capital: interest and dividends 4. Entrepreneur: profit
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
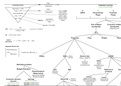
12. What does the circular flow diagram depict?
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
The circular flow model demonstrates how money moves through
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
society. Money flows from producers to workers as wages and
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
flows back to producers as payment for products. In short, an
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
economy is an endless circular flow of money. |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
1. Why is the concept of scarcity so important in economics?
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
Because the number of goods and services that can be produced
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
with them can be limited and there will never be enough
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
resources to meet everyone's needs. |\ |\ |\ |\
2. What does an individual's budget constraint identify?
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
all the possible combinations that you can afford within their
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
given income. |\
, 3. Identify two ways in which the budget constraint and the PPF
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
are similar and two ways in which they are different.
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
They are similar because they both assume resource and
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
technology are fixed and they both use two goods to simplify
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
assumptions. They are different because the budget constraint is |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
used by individuals and PPF is used by firms.
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
7. What does the PPF look like when resources are
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
homogeneous?
It is a straight line.
|\ |\ |\ |\
8. How does an increase in labor productivity change the PPF?
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
It moves to the right.
|\ |\ |\ |\
9. Define the term Opportunity Cost.
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\
It is what is given up when making a decision.
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\ |\
10. What causes increasing opportunity costs?
|\ |\ |\ |\ |\
Opportunity cost increases as production increases. |\ |\ |\ |\ |\