Which of the following should be the primary focus of early language intervention for at-risk
infants?
A.Establishing object permanence through play activities
B.Training primary caregivers to facilitate language learning
C.Creating readiness activities in the context of play
D.Enhancing social communication through play activities - Training primary caregivers to
facilitate language learning
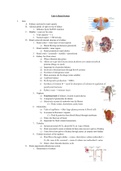
The figure above shows the oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal structures involved in swallowing.
Which of the following best describes the transit of the bolus at the moment depicted in the
figure? - B.The bolus is being propelled from the oral cavity by the tongue and has
entered the pharynx.
Primary motor innervation to the larynx and velum is provided by which cranial nerve? -
IX- Vagus Nerve
Fela is a third-grade student in a public school. She is a speaker of African American Vernacular
English (AAVE) who has difficulty with the Standard American English (SAE) dialect used in her
classroom. Her teacher believes that Fela's language skills are affecting her academic
performance and has referred her to the school's speech-language pathologist. Which of the
following is an appropriate rationale for providing language intervention for Fela?
A.It will likely foster better communication - Options (A), (B), and (C) are correct. The
intervention will foster better communication because Fela and her peers will have a common
dialect. Also, the intervention will provide Fela with the ability to switch easily between dialects
using SAE structures. Furthermore, being able to switch codes will enable Fela to participate in
more educational and vocational opportunities.
Federal laws regarding freedom of access to information stipulate that client records kept or
written by health care professionals can be
A.reviewed only by other health-care professionals
,B.reviewed only by the clients themselves unless the client provides written permission to share
with others
C.reviewed by anyone who submits a formal written request
D.released only by subpoena - B.reviewed only by the clients themselves unless the client
provides written permission to share with others
To justify providing individual treatment for a 2½ year old with apraxia of speech, which of the
following would be LEAST important for the SLP to include in the evaluation report?
A.A description of the child's typical interaction with peers
B.Relevant prognostic data
C.Information about apraxia of speech
D.A description of the language development of the child's older siblings - Option (D) is
correct. A description of the child's older siblings' language development does not provide the
objective, documented evidence required to justify provision of treatment for a child of an age
at which some unintelligibility would be typical.
The speech reception threshold (SRT) is a basic component of an evaluation of hearing function.
Which of the following statements about the SRT is most accurate?
A.It is measured in decibels and corresponds to the intensity level at which spondaic words can
be recognized approximately 50% of the time.
B.It makes use of test materials that are limited to monosyllabic words.
C.It provides information on how well speech is understood at conversational levels.
D.It is useful in validating acoustic i - A.It is measured in decibels and corresponds to the
intensity level at which spondaic words can be recognized approximately 50% of the time.
A clinician who employs active listening is doing which of the following?
A.Responding to both the content and the affect of the client's remarks
B.Listening very carefully and taking extensive notes
C.Conducting a clinician-directed interview
,D.Directing the client to specific answers to questions - Option (A) is correct. A clinician
who employs active listening responds to both the content (the denotative message) and the
affect (the emotional content) of a client's remarks.
This investigation was motivated by observations that when persons with dysarthria increase
loudness, their speech improves. Some studies have indicated that this improvement may be
related to an increase of prosodic variation. Studies have reported an increase of fundamental
frequency (F0) variation with increased loudness, but there has been no examination of the
relation of loudness manipulation to specific prosodic variables that are known to aid a listener
in parsing out meaningful informat - C.Vocal loudness
B.The prosody of persons with dysarthria may not show similar loudness effects.
C.A within-subjects design
A 55-year-old woman, recently hospitalized for probable cerebrovascular accident (CVA), is
referred for evaluation of stuttering speech. The initial conversation with the client indicates that
speech is characterized by frequent initial-phoneme repetitions and prolongations as well as
associated mildly effortful eye blinking. Which of the following pieces of information is crucial to
accurate speech diagnosis and decisions regarding management of the speech problem?
A.The site and extent of the - Option (C) is correct. Dysfluent speech may or may not be
directly caused by the patient's suspected CVA.
Which of the following is the best action to take initially with a client who presents with poor
oral control of liquids and solids, coughing and choking while eating and drinking, and a history
of hospitalizations associated with pneumonia?
A.Thickening liquids so that the client will be better able to control oral movements for
swallowing
B.Obtaining a modified barium-swallow study to determine appropriate interventions
, C.Evaluating the client's ability to eat a variety of foods in order to de - Option (B) is
correct. An assessment of the problem must be undertaken before treatment is provided, and
the best way to do this is to obtain a modified barium-swallow study.
A number of research reports have described poor auditory memory in children with language
impairments. Which of the following can most appropriately be concluded from these studies?
A.Poor auditory memory can be improved by language-intervention programs that focus on
teaching vocabulary and word meanings.
B.Poor auditory memory is a reflection of a language impairment, and clinicians and researchers
cannot effect improvement.
C.Poor auditory memory could be a reflection or a cause of a languag - Option (C) is
correct. Research reports are restricted to the variables examined in the studies on which they
are based. A relationship between poor auditory memory and language impairment has been
found in some research studies. Other factors could be involved, however, suggesting that
further research is needed. Conclusions about treatment or the effects of the impairment must
be made through additional research studies.
Ms. Brown, a 70-year-old retired female, was admitted to the hospital following a CVA. The SLP
conducted a comprehensive evaluation that revealed the presence of left-side neglect,
anosognosia (denial of impairment), and visuospatial problems, including prosopagnosia
(difficulty recognizing familiar faces). Although her auditory comprehension and repetition skills
were good, she experienced difficulty with topic maintenance and turn taking. Based on the
clinical features described, Ms. Brown's d - Option (C) is correct. The symptoms described
in the scenario are consistent with damage to the right hemisphere.
A client exhibits weakness, atrophy, and fasciculations of the right side of the tongue and lower
face. The client also has right vocal-fold weakness and nasal regurgitation of fluid when
swallowing. These problems are the result of damage to which part of the nervous system?
A.Brain stem
B.Cerebellum
C.Left cerebral cortex
D.Right cerebral cortex - A.Brain stem
***Why? -- Weakness, atrophy, fasciculations, and the other described symptoms are all
consistent with a lower motor neuron locus and suspected cranial nerve abnormalities (primarily
CN X and XII). These cranial nerves emerge directly from the brain stem and help mediate the