Knowledge clips - week 1
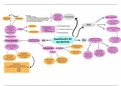
Conceptual model
Why? Help to visualize your research question and to provide a schematic overview of the
research. Build hypotheses and what type of analysis is suitable.
Defenitie van Conceptueel model: Are visual representations of relations between theoretical
constructs (variables) of interest (and typically also visualize the research question).
Variance can have different measurement scales:
Categorical (nominal, ordinal)
Quantitative (numbers)
ANOVA
Test main and moderating effect.
ANOVA helps us investigate with a certain level of confidence, what differences there might
be between groups. Of terwijl maakt het uit in welke groep je zit?
Voor ons idee. Gebaseerd op variance, dus how much explained by our predictor variable.
Are the mean scores statistically different?
ANOVA gebruiken indien OV = quantitative and PV = Categorical with more than 2 groups.
SSt (Total variance) = SSm (Variance explained by the model) + SSr (Unexplained variance)
Assumptions:
- Variance is homogeneous across groups
- Normally distributed
- Equally sized groups
- Object in only 1 group
Steps: niet voldaan dan ook niet verder naar volgende stap
1. Is data numerical & categorical
, 2. Whole make sense? F-test & R2
3. Which group means differ
R2
= bedrag in percentage
Hoe hoger des te beter (zoveel % explained by the model)
F-test
To investigate if the group means differ.
H0: μ1 = μ2 =....= μi
Ha: μi ≠ μj (there is a difference in the means, maar weten nog niet waar dus stap 3)
Stap 3:
, Knowledge clips 2
Moderation
Interaction = moderation
● The effect of one PV on the OV is moderated by another PV
● The effect of one PV on the OV depends on the level of another PV.
● PV’s interact in their effect on the OV.
For example:
Koffie pas zoet als je roert.
H0 by moderator = The effect of … on … is not moderated by …
H0 by moderator = The effect of … on … is moderated by …
Bij bovenstaande afbeelding: If the lines are not parallel, there is an interaction effect.
Factorial ANOVA: Calculations
With ANOVA, we are examining how much of the variance in our OV can be explained by
our PV.
With factorial ANOVA, we are examining how much of the variance in our OV can be
explained by multiple PV’s. (Want moderator)
We use factorial ANOVA when:
1. OV = Quantitative
2. PVs = Categorical
3. Independent groups (between-subject design) (Niet in meerdere groepen)
4. Variance is homogenous across groups
Steps:
1. Data suited for ANOVA? → Assumptions
2. Model as a whole makes sense? → F-test, R2
3. Individual PVs significant? → F-test per PV
4. Which group means differ? → Post hoc / follow up test
Conceptual model
Why? Help to visualize your research question and to provide a schematic overview of the
research. Build hypotheses and what type of analysis is suitable.
Defenitie van Conceptueel model: Are visual representations of relations between theoretical
constructs (variables) of interest (and typically also visualize the research question).
Variance can have different measurement scales:
Categorical (nominal, ordinal)
Quantitative (numbers)
ANOVA
Test main and moderating effect.
ANOVA helps us investigate with a certain level of confidence, what differences there might
be between groups. Of terwijl maakt het uit in welke groep je zit?
Voor ons idee. Gebaseerd op variance, dus how much explained by our predictor variable.
Are the mean scores statistically different?
ANOVA gebruiken indien OV = quantitative and PV = Categorical with more than 2 groups.
SSt (Total variance) = SSm (Variance explained by the model) + SSr (Unexplained variance)
Assumptions:
- Variance is homogeneous across groups
- Normally distributed
- Equally sized groups
- Object in only 1 group
Steps: niet voldaan dan ook niet verder naar volgende stap
1. Is data numerical & categorical
, 2. Whole make sense? F-test & R2
3. Which group means differ
R2
= bedrag in percentage
Hoe hoger des te beter (zoveel % explained by the model)
F-test
To investigate if the group means differ.
H0: μ1 = μ2 =....= μi
Ha: μi ≠ μj (there is a difference in the means, maar weten nog niet waar dus stap 3)
Stap 3:
, Knowledge clips 2
Moderation
Interaction = moderation
● The effect of one PV on the OV is moderated by another PV
● The effect of one PV on the OV depends on the level of another PV.
● PV’s interact in their effect on the OV.
For example:
Koffie pas zoet als je roert.
H0 by moderator = The effect of … on … is not moderated by …
H0 by moderator = The effect of … on … is moderated by …
Bij bovenstaande afbeelding: If the lines are not parallel, there is an interaction effect.
Factorial ANOVA: Calculations
With ANOVA, we are examining how much of the variance in our OV can be explained by
our PV.
With factorial ANOVA, we are examining how much of the variance in our OV can be
explained by multiple PV’s. (Want moderator)
We use factorial ANOVA when:
1. OV = Quantitative
2. PVs = Categorical
3. Independent groups (between-subject design) (Niet in meerdere groepen)
4. Variance is homogenous across groups
Steps:
1. Data suited for ANOVA? → Assumptions
2. Model as a whole makes sense? → F-test, R2
3. Individual PVs significant? → F-test per PV
4. Which group means differ? → Post hoc / follow up test