MODULE 12 COVERING OF THE TESTES
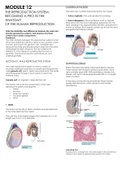
THE REPRODUCTION SYSTEM: The testes are covered and protected by two tissues.
BECOMING A PRO IN THE 1. Tunica vaginalis is the outer protective covering.
ANATOMY 2. Tunica albuginea is the inner fibrous coat or capsule.
Extensions from the tunica albuginea penetrate into the
OF THE HUMAN REPRODUCTION testis, dividing it into approximately 250-300 compartments
known as lobules. Each lobule contains up to four thin and
elongated seminiferous tubules.
State the similarities and differences between the male and
female reproductive systems, and propose why these
systems have similar components.
Feedback:
The main similarity between the reproductive systems is that
they have paired gonads (two testes or two ovaries), which
function to produce the gamete cells. Similarities exist
because the male and female systems arise from the same
embryological origin. However, the two systems are
different in many respects, including the structure of
gametes, hormonal production and influences, and
external genitalia.
SECTION 01: MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES
The male reproductive system involves a variety of
Within the testes are tightly coiled seminiferous tubules.
structures working in synchrony to create and transport the
These tubules are the sperm producing factories. Each
male gamete cell, sperm. Sperm are produced in the testes
testis contains about 600-1000 seminiferous tubules in its
and transported through a duct system to reach the
lobules, with each tubule approximately 80 c m in length
external world.
when uncoiled.
Gamete cell: An organism’s reproductive cell
In the loose connective tissue between these tubules,
Leydig cells are found, which produce and secrete
This section will cover the components of the male
testosterone.
reproductive system including the:
• Testes
• Scrotum
• Male duct system
• Accesory glands
• Penis
1. TESTES
The testes are the site of sperm creation and development
in the male reproductive system.
They are two oval-shaped organs that measure 4-5 c m in
length and 2.5-3 c m in diameter.
Interesting Fact
If spread out in a straight line, the total length of the seminiferous
tubules in both testes is approximately equal to 0.5 miles!
, SPERM MUSCLES OF THE SCROTUM
Sperm are gametes of the male reproductive system, and There are two muscles in the scrotum. These muscles
carry the paternal genetic information. function to control the temperature of the testes.
Sperm can be organized into four regions.
Dartos Muscle
This muscle is located superficially in the skin of the scrotum.
It is responsible for the rugose (wrinkly) appearance of the
scrotal sac, and helps to regulate temperature by altering
the exposed surface area of the scrotum.
Cremaster Muscle
The cremaster muscle is a covering of the testis found deep
to the scrotal wall. It reflexively contracts in a cold
environment, drawing the testes superiorly in the scrotum,
closer to the body wall where they can absorb body heat.
1. Head
The head is flat and has an oval shape. It contains the
nucleus, which contributes either an X or Y chromosome to
the fertilization process. The head also contains the
acrosomal cap, which contains enzymes that are released
prior to fertilization to help the sperm penetrate the layers
of the egg.
2. Neck
The neck connects the head to the midpiece.
3. Midpiece
The midpiece is a continuation of the neck with a
mitochondrial collar that helps produce energy.
4. Tail
The tail, or flagellum, is the source of movement for the
sperm.
Interesting Fact
The average volume of ejaculate is 2-5 m l with approximately 15-
200 million sperm per ml.
2. SCROTUM 3. MALE DUCT SYSTEM
The scrotum is the sac of skin and fascia surrounding the Following production in the testes, the sperm must travel
testes. It is derived from the anterior abdominal wall and through the duct system to pass out of the body. The right
resides outside of the abdominopelvic cavity. and left testes each have their own duct systems.
a. Epididymis
b. Vas Deferens
c. Urethra
THE REPRODUCTION SYSTEM: The testes are covered and protected by two tissues.
BECOMING A PRO IN THE 1. Tunica vaginalis is the outer protective covering.
ANATOMY 2. Tunica albuginea is the inner fibrous coat or capsule.
Extensions from the tunica albuginea penetrate into the
OF THE HUMAN REPRODUCTION testis, dividing it into approximately 250-300 compartments
known as lobules. Each lobule contains up to four thin and
elongated seminiferous tubules.
State the similarities and differences between the male and
female reproductive systems, and propose why these
systems have similar components.
Feedback:
The main similarity between the reproductive systems is that
they have paired gonads (two testes or two ovaries), which
function to produce the gamete cells. Similarities exist
because the male and female systems arise from the same
embryological origin. However, the two systems are
different in many respects, including the structure of
gametes, hormonal production and influences, and
external genitalia.
SECTION 01: MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES
The male reproductive system involves a variety of
Within the testes are tightly coiled seminiferous tubules.
structures working in synchrony to create and transport the
These tubules are the sperm producing factories. Each
male gamete cell, sperm. Sperm are produced in the testes
testis contains about 600-1000 seminiferous tubules in its
and transported through a duct system to reach the
lobules, with each tubule approximately 80 c m in length
external world.
when uncoiled.
Gamete cell: An organism’s reproductive cell
In the loose connective tissue between these tubules,
Leydig cells are found, which produce and secrete
This section will cover the components of the male
testosterone.
reproductive system including the:
• Testes
• Scrotum
• Male duct system
• Accesory glands
• Penis
1. TESTES
The testes are the site of sperm creation and development
in the male reproductive system.
They are two oval-shaped organs that measure 4-5 c m in
length and 2.5-3 c m in diameter.
Interesting Fact
If spread out in a straight line, the total length of the seminiferous
tubules in both testes is approximately equal to 0.5 miles!
, SPERM MUSCLES OF THE SCROTUM
Sperm are gametes of the male reproductive system, and There are two muscles in the scrotum. These muscles
carry the paternal genetic information. function to control the temperature of the testes.
Sperm can be organized into four regions.
Dartos Muscle
This muscle is located superficially in the skin of the scrotum.
It is responsible for the rugose (wrinkly) appearance of the
scrotal sac, and helps to regulate temperature by altering
the exposed surface area of the scrotum.
Cremaster Muscle
The cremaster muscle is a covering of the testis found deep
to the scrotal wall. It reflexively contracts in a cold
environment, drawing the testes superiorly in the scrotum,
closer to the body wall where they can absorb body heat.
1. Head
The head is flat and has an oval shape. It contains the
nucleus, which contributes either an X or Y chromosome to
the fertilization process. The head also contains the
acrosomal cap, which contains enzymes that are released
prior to fertilization to help the sperm penetrate the layers
of the egg.
2. Neck
The neck connects the head to the midpiece.
3. Midpiece
The midpiece is a continuation of the neck with a
mitochondrial collar that helps produce energy.
4. Tail
The tail, or flagellum, is the source of movement for the
sperm.
Interesting Fact
The average volume of ejaculate is 2-5 m l with approximately 15-
200 million sperm per ml.
2. SCROTUM 3. MALE DUCT SYSTEM
The scrotum is the sac of skin and fascia surrounding the Following production in the testes, the sperm must travel
testes. It is derived from the anterior abdominal wall and through the duct system to pass out of the body. The right
resides outside of the abdominopelvic cavity. and left testes each have their own duct systems.
a. Epididymis
b. Vas Deferens
c. Urethra