Topic 1 – Cell Biology
Table of Content
1.1 Cell structure .................................................................... 2
1.1.1 Eukaryotes and prokaryotes .......................................................................................2
1.1.2 Animal and plant cells .................................................................................................2
1.1.3 Cell specialisation ........................................................................................................3
1.1.4 Cell differentiation ......................................................................................................5
1.1.5 Microscopy..................................................................................................................5
1.1.6 Culturing microorganisms (biology only) ....................................................................5
1.2 Cell division ...................................................................... 6
1.2.1 Chromosomes .............................................................................................................6
1.2.2 Mitosis and the cell cycle ............................................................................................6
1.2.3 Stem cells ....................................................................................................................7
1.3 Transport in cells .............................................................. 8
1.3.1 Diffusion ......................................................................................................................8
1.3.2 Osmosis .......................................................................................................................9
1.3.3 Active transport ........................................................................................................10
1
, AQA GCSE Biology notes Topic 1 – Cell Biology
1.1 Cell structure
1.1.1 Eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Eukaryotic cell
• Animal, plant, fungi
• Has a cell membrane, cytoplasm & genetic material enclosed in a nucleus
• More complex
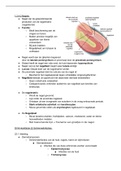
1.1.2 Animal and plant cells
Animal cell
Nucleus • Contains genetic material (DNA)
• Control cell's activities
Mitochondria • Where aerobic respiration takes place
• Releasing energy for cells to work
Cytoplasm • Gel-like substance
• Where chemical reaction takes place
• Contains enzymes to control chemical reaction
Ribosome • Where protein synthesis happens
• Make proteins using amino acids
Cell membrane • Hold cells together
• Controls movement of substances in & out of cell
Plant cell
Cell wall • Supports & strengths cell by cellulose
Permanent vacuole • Contains air sap (weak solution of sugar & salt)
• Keep cells rigid to support plant
Chloroplast • Contains chlorophyll that absorb light for photosynthesis
• Where photosynthesis occurs
2
, AQA GCSE Biology notes Topic 1 – Cell Biology
Prokaryotic cells
• Bacteria
• Have cytoplasm & cell membrane surround by cell wall
• Genetic material is not enclosed in a nucleus
• Its DNA is found as a loop in the cell & there may be one or more plasmids
Why are prokaryotic cells smaller & simpler?
• Larger SA : volume ratio
• Short diffusion distance
• Allow sufficient transport of molecules into & out of cell to meet needs of organism
Bacteria cell
Slime capsule • Protect cell
Plasmid • A small ring of DNA
Flagellum • Move themselves
around
1.1.3 Cell specialisation
• Specialisation – cell differentiate to become specialized
Animal cells
Nerve cells Function
• Transmit electrical impulses around the body
Adaptation
• Have lots of dendrites to connect other nerve cells
• Axon is very long to cover more distance
• Synapses contain lots of mitochondria to provide energy
to make transmitter chemicals
• Myelin act as an electrical insulator to stop electrical
impulse from leaking out
Muscle cells Function
• Contract and relax to bring about movement
Adaptation
• Contain protein fibre to change length of cell (↓fibre
↓length)
• Contain many mitochondria to provide energy for
contraction and respiration
• Store glycogen which can be broken down in cellular
respiration to transfer energy
Sperm cells Function
• Carry father’s genetic information and fertilise the egg
Adaptation
• Have long tails & streamlined to help swim to egg &
reduce cells energy requirements to travel to egg
• Acrosome contain digestive enzymes to break through egg
cell membrane
3
, AQA GCSE Biology notes Topic 1 – Cell Biology
• Nucleus contains DNA / 1 set of chromosome to be passed
on & preserves the chromosome no when the egg is
fertilised
• Nucleus contains 23 chromosomes
• Mid-section contains mitochondria to provide energy in
respiration for tail to work
Plant cells
Root hair cells Function
• To absorb water by osmosis & mineral ions by active
transport from soil efficiently
Adaptation
• Have large SA to absorb water & mineral ions
• Have large permanent vacuole to speed up movement of
water by osmosis
• Contain mitochondria to provide energy to transport
mineral ions into cell
Xylem cells Function
• Transport water & mineral ions from root to stems &
leaves
Adaptation
• Have strong lignin spirals which allow them to withstand
water pressure to transport water in transpiration stream
& support plant stem
• Cell die & form long hallow tube which is strengthened by
lignin spirals allow water & mineral ions to move up easily
• Few cell structures & so they are dead for more space &
supported by lignin
Phloem cells Function
• Transport dissolved sugar through translocation from
leaves to rest of plant for immediate use or storage
Adaptation
• Cell walls between cells break down to form sieve plates -
allow water carrying dissolved food move freely up &
down tube to where it's needed
• Companion cells keep them alive & contain mitochondria
to provide energy to move dissolved food up & down plant
4