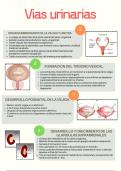
Lecture 9: Muscle Contraction
Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Membrane potentials
● Inside of the membrane is usually around -60 to -90mV, relative to the outside
○ Neurons and muscle cells can use their membrane potentials to generate
electrical signals
○ This is achieved by opening and closing specialized proteins in the
membrane called ion channels
Excitation-contraction coupling = for a skeletal muscle fibre to contract, its
membrane must first be “excited”, in other words, it must be stimulated to
fire an action potential
● The muscle fibre action potential, which sweeps along the sarcolemma as a
wave, is “coupled” to actual contraction through the release of calcium ions
from the SR
● Once released, the calcium interacts with the shielding proteins, forcing them
to move aside so that the actin-binding sites are available for attachment by
myosin heads
● The myosin then pulls the actin filaments toward the centre, shortening the
muscle fibre
Excitation-Contraction Coupling: The Neuromuscular junction
● The neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron
and a muscle fibre
○ It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fibre,
causing muscle contraction
, Process of Synaptic Transmission
1) Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action
potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates
voltage-gated calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron
2) Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles,
triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent
neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft
3) In vertebrates, motor neurons release neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh)
which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine
receptors (NAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fibre, also known as
the sarcolemma
4) nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning that they serve as ligand-gated ion
channels. The binding of Ach to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fibre
causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.
E-C Coupling: Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (Calcium Storage)
● Primary site of calcium release
● The SR contains ion channel pumps within its membrane that are responsible
for pumping calcium ions into the SR
● As the calcium ion concentration within the SR is higher than in the rest of the
cell, the calcium ions won’t freely flow into the SR, and therefore pumps are
required, that use energy, which they gain from a molecule called adenosine
triphosphate (ATP)
● These calcium pumps are called Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum ATPases
(SERCA).
E-C Coupling: Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (Calcium Release)
● Calcium ion release from the SR occurs in the junctional SR/terminal
cisternae through a ryanodine receptor and is known as a calcium spark
● There are three types of ryanodine receptor (RyR1) (in skeletal muscle),
RyR2 (in cardiac muscle) and RyR3 (in the brain)
Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Membrane potentials
● Inside of the membrane is usually around -60 to -90mV, relative to the outside
○ Neurons and muscle cells can use their membrane potentials to generate
electrical signals
○ This is achieved by opening and closing specialized proteins in the
membrane called ion channels
Excitation-contraction coupling = for a skeletal muscle fibre to contract, its
membrane must first be “excited”, in other words, it must be stimulated to
fire an action potential
● The muscle fibre action potential, which sweeps along the sarcolemma as a
wave, is “coupled” to actual contraction through the release of calcium ions
from the SR
● Once released, the calcium interacts with the shielding proteins, forcing them
to move aside so that the actin-binding sites are available for attachment by
myosin heads
● The myosin then pulls the actin filaments toward the centre, shortening the
muscle fibre
Excitation-Contraction Coupling: The Neuromuscular junction
● The neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron
and a muscle fibre
○ It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fibre,
causing muscle contraction
, Process of Synaptic Transmission
1) Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action
potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates
voltage-gated calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron
2) Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles,
triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent
neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft
3) In vertebrates, motor neurons release neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh)
which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine
receptors (NAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fibre, also known as
the sarcolemma
4) nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning that they serve as ligand-gated ion
channels. The binding of Ach to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fibre
causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.
E-C Coupling: Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (Calcium Storage)
● Primary site of calcium release
● The SR contains ion channel pumps within its membrane that are responsible
for pumping calcium ions into the SR
● As the calcium ion concentration within the SR is higher than in the rest of the
cell, the calcium ions won’t freely flow into the SR, and therefore pumps are
required, that use energy, which they gain from a molecule called adenosine
triphosphate (ATP)
● These calcium pumps are called Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum ATPases
(SERCA).
E-C Coupling: Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (Calcium Release)
● Calcium ion release from the SR occurs in the junctional SR/terminal
cisternae through a ryanodine receptor and is known as a calcium spark
● There are three types of ryanodine receptor (RyR1) (in skeletal muscle),
RyR2 (in cardiac muscle) and RyR3 (in the brain)