The brain works as part of the central nervous system with the spinal cord. All vertebrates have a CNS.
Other nerves use the peripheral nervous system, which stretches out from your brain and spinal cord to
every other part of the body, and this includes sensory and motor nerves.
The brain has 2 halves, called hemispheres. These are linked by the corpus callosum, which lets the left
and right hemispheres communicate. The hemispheres are not symmetrical as the left and right specialise
in different things, this is called brain lateralisation.
The left hemisphere controls the right side of the body, and vice versa.
Left side of the brain – controls language, reasoning, numbers, abstract thought, and spatial
awareness
Right side of the brain – musical ability and creativity
In most people, one side of the brain is more dominant than the other
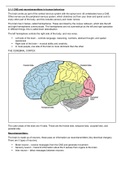
THE CEREBRAL CORTEX:
The outer areas of the brain are 4 lobes. These are the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, and
parietal lobe.
Neurotransmitters:
The brain is made up of neurons, these pass on information as neurotransmitters (tiny electrical charges).
There are 3 types of neurons;
Motor neuron – receive messages from the CNS and generate movement
Sensory neuron – transmit information about the 5 senses from organs to the brain
Inter neuron – takes messages between neurons
,A neuron has a cell body with a nucleus in the middle of it. There are dendrites around the outside, these
pick up information from other cells, turning it into electric signals. An electrical charge travels down the
axon and passes on to the dendrites of the next cell.
There are different neurotransmitters, each with different functions:
Noradrenaline – produces attention and triggers the fight or flight response in people. Those who
have ADHD benefit from being prescribed this
Dopamine – linked to pleasure and addiction feelings. Drugs that block dopamine receptors seem
to reduce the symptoms of schizophrenia
Serotonin – neurotransmitter for happiness. Drugs that boost serotonin by inhibiting reuptake of
serotonin can reduce depression
Neurotransmitters act very fast and very quickly.
1. Serotonin is linked with mood and sadness, low levels of this increase aggression
2. Dee Higley in 1996 studied rhesus monkeys and measured 5HIAA (serotonin), he found monkeys
with low serotonin were more risk taking and aggressive on the whole than others
3. Dopamine is linked to attention and pleasure, increased levels of dopamine can lead to increased
rates of aggression
4. In 2013, Ferrari studied rats, he allowed them to fight every day for 10 days, at the same time. On
the 11th day, he did not allow the rats to fight (did not put an intruder rat in the cage), but when the
rats neurotransmitters were measured, he found a drop in serotonin and dopamine was increased,
indicating the rats were anticipating a fight
Low serotonin and high dopamine = aggression
Synapse
This is the gap between neurons. Neurotransmitters float across the synaptic gap until they are picked up
by special dendrite receptors on the next neuron, here they are converted back into electrical signals for
the next neuron.
, Re-uptake is where a neurotransmitter does not attach itself to a receptor and is recycled. If this is
prevented then a neurotransmitter will stay longer in a synapse trying to pass on a message. This is how
some depression medicines work, SSRI’s (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) boost serotonin in the
brain, which can improve mood.
3.1.2 Effect of recreational drugs on transmission process in CNS
Recreational drugs alter a person’s cognitions, making experiences enjoyable. Recreational drugs are
also known as psychoactive drugs, because they impact the CNS.
The reward pathway is influenced when drugs are taken -> this is the route used by dopamine.
Dopamine creates feelings of pleasure and a desire to repeat the activity (this is generated by feelings of
sex, eating and drinking)
Some neurons are dopaminergic, this means they generate and respond to dopamine. The pathway of
dopaminergic neurons leads to the pleasure centre. It is made up of the mesolimbic pathway, which flows
through the limbic system, generating feelings of satisfaction, contentment and euphoria.
1. Agonists – some drugs imitate natural neurotransmitters (nicotine, cannabis, heroin), this fools the
brain into activating the pleasure centres. These drugs are more powerful than most naturally
occurring neurotransmitters.
2. Antagonists – other drugs (amphetamines) boost the amount of normal neurotransmitters,
triggering the brains pleasure centres.
Desensitisation – over time a larger amount of drugs are needed to get a pleasurable feeling from the
drug
Addiction – without the drug, the brain is not generating enough dopamine, so the user feels unhappy
without it
Nicotine
This is the psychoactive chemical in cigarettes
It mimics acetylcholine (natural neurotransmitter)
Enters the blood when inhaled, arrives in the brain and attaches to acetylcholine receptors
The receptors excite the neuron, causing it to release dopamine -> excites the neighbouring
neurons in the reward pathway, generating feelings of pleasure
The brain is plastic, this means it changes in structure. If nicotine receptors are overused, then the brain
responds by cutting back on nearby dopamine receptors -> this means more dopamine is needed to give
a normal level of functioning. This is how addiction starts.
Cocaine (an amphetamine)
This impacts the reward pathway in the brain and blocks re-uptake of neurons
In a normal brain for example, dopamine is reabsorbed back into neurons
Cocaine attaches to a reuptake receptor, “blocking” it -> this stops dopamine from being
reabsorbed back into the neuron and so levels of dopamine in the synaptic gap build
Natural dopamine occurs, but it is in massive quantities
Desensitisation and addiction occur with extended use of cocaine.
Credibility Olds and Milner studied rats, connecting wire to the pleasure centre in the brain.
Using electricity they could give the brain a pleasurable shock, through pressing a
lever. The rats pressed this lever, and kept returning, ignoring other sources of
pleasure
Stralker and Mackie (2005) studied mice, giving them cannabinoid receptors.
They showed similar behaviours to humans when they were given cannabis
Has face validity form observations and self reports of drug users