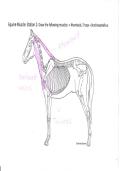
Single = between 2 bones
Compound = between 2 or more bones
Function:
- Hold skeleton together
- Support movement
Classification:
Functional Structural
Synarthroses = immovable e.g. sutures in skull Fibrous – held together by fibrous connective
tissue – do not move e.g. sutures skull
Amphiarthroses = slightly moveable e.g. Cartilaginous – bones connected by cartilage. 2
inbetween vertebrae subdivisions = hyaline (synchondroses +
symphyses) and fibrocartilaginous (symphyses)
Diarthroses = freely moveable e.g. elbow Synovial – have a space between the bones
called synovial/joint cavity, filled with synovial
fluid e.g. pelvis symphysis
Fibrous:
- Sutures = skull, bind, mostly synarthroses
- Syndesmoses = slight degree movement, thicker bands of fibrous tissue, e.g. between splint
bones
- Gomphoses = immovable, between teeth roots and alveolar process of maxilla and mandible
Cartilaginous:
- Primary = synchondroses, hyaline cartilage, e.g. diaphysis to epiphysis via epiphyseal plate,
cartilage ossifies when growth ceases = syntosis
- Secondary = flat disc fibrocartilage unites articulating surfaces, sightly moveable e.g. pubic
symphysis
Synovial:
- Dense irregular connective tissue
- Synovial fluid = viscous, yellow fluid, contains hyaluronic acid and interstitial fluid, lubricates
joint, reduces friction, maintains joint health via chondrocytes
- Synovial cartilage
- Articular cartilage = smooth, white tissue covers ends of bones, organic matrix – type 2
collagen, smooth and lubricated to allow gliding, absorbs shock, no nerve, blood or lymph
supply
- Articular capsule = holds joint together and protects
- Movement:
- Arthrodial = planar gliding movement e.g. distal carpal joints