GUIDELINES IN PRIMARY CARE, 4TH EDITION
bn bn bn bn bn
Amelie Hollier
b n
,Clinical Guidelines in Primary Care 4th Edition Hollier Test Bank
bn b n bn b n b n b n b n bn b n
Table of Contents
b n b n
Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Disorders
bn bn bn
Chapter 2: Dermatologic Disorders
bn bn b n
Chapter 3: Ear Nose & Throat Disorders
bn bn bn bn bn b n
Chapter 4: Endocrine Disorders
bn bn bn
Chapter 5: Gastrointestinal Disorders
bn bn bn
Chapter 6: Genetic Disorders
bn bn bn
Chapter 7: Health Promotion - Pediatric
bn bn bn bn bn
Chapter 8: Hematologic Disorders
bn bn bn
Chapter 9: Lactation and Breastfeeding
bn bn bn b n
Chapter 10: Men’s Health Disorders
bn bn bn bn
Chapter 11: Neurologic Disorders
bn bn b n
Chapter 12: Ophthalmic Disorders
bn bn bn
Chapter 13: Orthopedic Disorders
bn bn bn
Chapter 14: Pregnancy
bn bn
Chapter 15: Psychiatric Disorders, Violence, Abuse, Neglect
bn bn bn bn bn bn
Chapter 16: Pulmonary Disorders
bn bn bn
Chapter 17: Sexually Transmitted Diseases
bn bn bn bn
Chapter 18: Urologic Disorders
bn bn bn
Chapter 19: Women’s Health Disorders
bn bn bn bn
,Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Disorders
bn b n b n
Clinical Guidelines in Primary Care 4th Edition Test bank
b n b n b n b n bn b n b n b n
MULTIPLE CHOICE b n
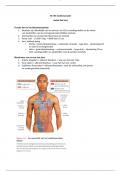
1. The nurse is aware that the muscle layer of the heart, which is
bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn
responsible for the heartscontraction, is the:
bn bn bn bn bn bn
a. endocardium.
b. pericardium.
c. mediastinum.
d. myocardium.
ANS: D bn
The myocardium is the specialized muscle layer that allows the heart to
bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn
b n contract.2.The nurse clarifies that the master pacemaker of the heart is
bn bn b n bn bn bn b n bn bn bn
b n the:
a. left ventricle.
bn
b. atrioventricular (AV) node. bn bn
c. sinoatrial (SA) node. bn bn
d. bundle of His. bn bn
ANS: C bn
The SA node is the master pacemaker of the heart.
bn bn bn b n bn bn bn bn bn
3. The nurse is aware that the symptoms of an impending myocardial
b n b n b n b n b n b n b n b n b n b n
infarction (MI) differ in women because acute chest pain is not present.
b n b n b n bn b n bn b n b n bn b n b n bn
bnWomen are frequently misdiagnosed as having:
bn bn bn b n bn
a. hepatitis A. bn
b. indigestion.
c. urinary infection. bn
d. menopausal complications. bn
, ANS: B bn
Indigestion, gallbladder attack, anxiety attack, and depression are frequent misdiagnoses
bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn
bnforwomen having an MI. bn bn bn
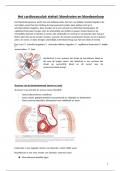
4. The nurse identifies the LUBB sound of the LUBB/DUBB of the cardiac
b n b n b n bn bn b n bn bn b n bn b n
bn cycle as the sound ofthe:
bn b n bn b n
a. AV valves closing.
bn bn
b. closure of the semilunar valves.
bn bn bn bn
c. contraction of the papillary muscles. bn bn bn bn
d. contraction of the ventricles. bn bn bn
ANS: A bn
The LUBB is the first sound of a low pitch heard when the AV valves close.
bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn
5. A patient is admitted from the emergency department. The emergency
b n b n b n b n b n b n b n b n b n
b n department physician notes the patient has a diagnosis of heart failure with a New
bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn
bn York Heart Association (NYHA)classification of IV. This indicates the patients
bn bn b n b n b n b n b n b n bn
b n condition as: bn
a. moderate heart failure. bn bn
b. severe heart failure. bn bn
c. congestive heart failure. bn bn
d. negligible heart failure. bn bn
ANS: B bn
Class IV: Severe; patient unable to perform any physical activity without
bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn
discomfort. Angina orsymptoms of cardiac inefficiency may develop at rest.
bn bn b n b n b n b n bn bn b n bn
6. The nurse assesses that the home health patient has no signs or symptoms
b n bn bn bn b n b n bn b n b n bn b n bn
b n of heart failure, butdoes have a history of rheumatic fever and has been
bn bn bn b n bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn
bn recently diagnosed with diabetes mellitus.The nurse is aware that using the
b n b n bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn
bn American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association
bn bn bn bn bn b n b n b n
b n (ACC/AHA) staging, this patient would be a: b n b n b n b n b n b n
a. stage A. bn
b. stage B. bn
c. stage C. bn
d. stage D. bn
ANS: A bn
The ACC/AHA staging describes stage A as a person without symptoms of heart
bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn bn
failure, butwith primary conditions associated with the development of the disease.
bn bn bn bn b n b n bn b n b n bn b n