DNA, Nucleic Acids and Nucleotides
Two Types of Nucleic Acids
There are two types of nucleic acids:
1. RNA (ribonucleic acid)
2. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
Chemical Composition of Nucleotides, DNA, and RNA
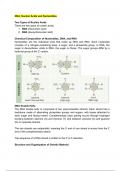
Nucleotides are the individual units that make up DNA and RNA. Each nucleotide
consists of a nitrogen-containing base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. In DNA, the
sugar is deoxyribose, while in RNA, the sugar is ribose. The sugar groups differ by a
hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon.
DNA Double Helix
The DNA double helix is composed of two polynucleotide strands. Each strand has a
backbone made of alternating phosphate groups and sugars, with bases attached to
each sugar and facing inward. Complementary base pairing occurs through hydrogen
bonding between adenine (A) and thymine (T) and between cytosine (C) and guanine
(G) on opposite strands.
The two strands are antiparallel, meaning the 5' end of one strand is across from the 3'
end of the complementary strand.
The sequence of a DNA strand is written in the 5' to 3' direction.
Structure and Organization of Genetic Material
Two Types of Nucleic Acids
There are two types of nucleic acids:
1. RNA (ribonucleic acid)
2. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
Chemical Composition of Nucleotides, DNA, and RNA
Nucleotides are the individual units that make up DNA and RNA. Each nucleotide
consists of a nitrogen-containing base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. In DNA, the
sugar is deoxyribose, while in RNA, the sugar is ribose. The sugar groups differ by a
hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon.
DNA Double Helix
The DNA double helix is composed of two polynucleotide strands. Each strand has a
backbone made of alternating phosphate groups and sugars, with bases attached to
each sugar and facing inward. Complementary base pairing occurs through hydrogen
bonding between adenine (A) and thymine (T) and between cytosine (C) and guanine
(G) on opposite strands.
The two strands are antiparallel, meaning the 5' end of one strand is across from the 3'
end of the complementary strand.
The sequence of a DNA strand is written in the 5' to 3' direction.
Structure and Organization of Genetic Material