Gene Expression & Central Dogma
Gene Expression
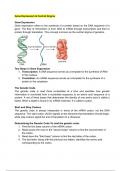
Gene expression refers to the synthesis of a protein based on the DNA sequence of a
gene. The flow of information is from DNA to mRNA through transcription and then to
protein through translation. This concept is known as the central dogma of genetics.
Two Steps in Gene Expression
1. Transcription: A DNA sequence serves as a template for the synthesis of RNA
in the nucleus.
2. Translation: An mRNA sequence serves as a template for the synthesis of a
protein in the cytoplasm.
The Genetic Code
The genetic code is read three nucleotides at a time and specifies how genetic
information is converted from a nucleotide sequence to an amino acid sequence of a
protein. A set of three bases that determines the identity of one amino acid is called a
triplet. When a triplet is found in an mRNA molecule, it is called a codon.
Start and Stop Codons
The genetic code is always interpreted in terms of the mRNA codon, not the DNA
sequence. The start codon (AUG) signals to the ribosome that translation should begin,
while stop codons signal the end of translation to a ribosome.
Determining the Genetic Code To read the genetic code:
1. Find the first base column of the mRNA codon.
2. Read across the rows in the "second base" column to find the second letter of
the codon.
3. Read down the "third base" column to find the last letter of the codon.
4. The last letter, along with the previous two letters, identifies the amino acid
corresponding to the codon.
Gene Expression
Gene expression refers to the synthesis of a protein based on the DNA sequence of a
gene. The flow of information is from DNA to mRNA through transcription and then to
protein through translation. This concept is known as the central dogma of genetics.
Two Steps in Gene Expression
1. Transcription: A DNA sequence serves as a template for the synthesis of RNA
in the nucleus.
2. Translation: An mRNA sequence serves as a template for the synthesis of a
protein in the cytoplasm.
The Genetic Code
The genetic code is read three nucleotides at a time and specifies how genetic
information is converted from a nucleotide sequence to an amino acid sequence of a
protein. A set of three bases that determines the identity of one amino acid is called a
triplet. When a triplet is found in an mRNA molecule, it is called a codon.
Start and Stop Codons
The genetic code is always interpreted in terms of the mRNA codon, not the DNA
sequence. The start codon (AUG) signals to the ribosome that translation should begin,
while stop codons signal the end of translation to a ribosome.
Determining the Genetic Code To read the genetic code:
1. Find the first base column of the mRNA codon.
2. Read across the rows in the "second base" column to find the second letter of
the codon.
3. Read down the "third base" column to find the last letter of the codon.
4. The last letter, along with the previous two letters, identifies the amino acid
corresponding to the codon.