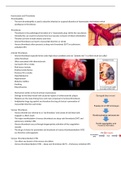
(FLUKES)
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Trematodes are macroscopic visible parasites and belong to the phylum of the platyhelminths. The lifecycle of
the trematodes is typically an indirect cycle, meaning at least 2 different species are involved.
General characteristics
o Parasitic in vertebrates
o Global distribution: determined by the presence of intermediate host and habits of people
o As adult or juvenile in diverse organ systems: mostly GI and respiratory system
o At least 2 hosts (indirect cycle) with different generations
o Flukes: Digenea
o Host specificity:
High specificity for ‘gastropod’ 1st intermediate host (snails)
Low specificity for vertebrate final host or 2nd intermediate host
General morphology
o Dorso-ventrally flattened
o Non-segmented (<-> cestode)
o Bilateral symmetry
o Coelome, anus and circulation system absent
o Excretion system based on flame cells
o Incomplete digestive system: have pharynx but no anus
blind intestine: ends in caeca
o Mostly hermaphrodite: have both male and female
reproductive organs
Exemption: schistosoma
External structures:
o Ventral suckers: used to adhere on surface + to move the parasite around
o Oral suckers: also uptake of nutrients
o Tegument: syncytium of cells (continuous layer with no boundaries)
Structure maintained by:
subtegumental cells
circular + longitudinal muscles important for the function of the tegument (see
Praziquantel)
Has spines on the surface: spine can cause tissue damage/inflammation
Very fast turnover of tegument cells: constantly dividing
Uptake of nutrients via tegument is possible: absorption of low MW nutrients (sugars/AA)
Secretion of proteases via vesicles: proteolytic degradation of proteins
possible to take up AA
Protection against EC factors + immune escape:
, covered by glycosylated molecules (not VSG)
antigenic shedding
Internal structures:
o Reproductive organs: most developed system of all systems in the parasite
Hermaphrodite: so both ovary and testis (except schistosomes!)
Fertilization: cross-fertilization (2 individuals that will fertilize)
Testis: sperm has 2 flagella
ovary:
parasite can store the sperm in receptaculum siminis
parasite produces 1 fertilized egg/minute
genital pore: release of eggs
Mehlis glands: produce egg shell (resistance of eggs in the environment)
o Digestive system: incomplete
Blind intestine
Ends in the caeca
o Nervous system: ladder-type
Some stages of parasite: light-sensitive ‘eye-spots’, give the parasites a phototropic activity
(move towards light)
o Muscular tissue: subtegumental (see tegument)
Limited motility of parasites not determined by muscles but by the ventral suckers
Basis of activity of Praziquantel
Note: All flukes can be treated by Praziquantel (both larval as adult stages). Praziquantel will affect the
intracellular Ca signalling, this will paralyse the muscles of the integument. When the muscles are paralysed,
there will be no sufficient turn-over of the tegument cells then there is no uptake of nutrients or attachment
of the parasite anymore. The only one that cannot be treated by praziquantel is Echinostomatida Fasciola. This
one needs to be treated with triclabendazole.
Standard life cycle
Characteristic alternation of asexual multiplication in the (mollusk) invertebrate (for colonization of the
intermediate host), followed by sexual multiplication in the vertebrate host.
o Zygote: fertilized egg excreted by adult worm (1 egg/minute)
Operculum: cap on the egg that can come off and will release the miracidia
This is the point where the miracidium will leave the egg
No feeding process so no uptake of nutrients
o Miracidium: ciliated fee-living larva that infects the mollusk (active or passive)
Mollusk: invertebrate first intermediate host
No feeding process so no uptake of nutrients
o Sporocyst: produces dividing germinal cells, sometimes formation of 2 nd generation sporocyst
Life stage in the mollusk, formed almost right after the uptake by the mollusk
No cilia
Produces germinal cells that proliferate and exit the sporocyst via the escape glands
Some limited uptake of nutrients through the sporocyst wall by diffusion
o Redia: larval intermediate stage of germinal cells, sometimes formation of daughter generations
Life stage in the mollusk
Produces germinal cells that proliferate and exit the redia via the escape glands
Target primitive liver and pancreas of the snail
, SO redia and sporocysts: asexual multiplication just by germinal tissue that proliferates, gives rise to daughter
generations. Big difference: in redia you already have a mouth, pharynx and caeca and thus will feed.
o Cercaria:
Larva with tail: to escape the mollusk
Reproductive organs partially present: not fully developed but basis
Leave the mollusk actively
can become cyst in environment or can go to next intermediate host
o Metacercaria: infectious cyst form (free or in >= 2 nd intermediate host) in the environment
Can penetrate skin of second intermediate host: e.g. are eaten by fish, when they invade
the skin of fish they become metacercaria
Can stay in the environment as cyst: e.g. on water plants and can encyst on the plants so
become metacercaria
Furocercaria in Schistosoma: immediate active skin penetration in the human host
Cercaria immediate penetrate the human host
No second intermediate host, no cyst stage
Note: in the winter the parasite will either sit in the mollusk (sporocyst/redia) or is in a cyst in the fish tissue or
on plant material. This is important for the survival of the parasite.
*highest situation is typical for schistosomes: from sporocyst to daughter sporocyst to immediately cercaria
cercariae of schistosomes = furcocercariae:
- have a Y-shaped tail: enables them to swim
- have light-sensitive dots: enables them to be phototropic
, once they touch skin of a human host, enzymes produced on anterior part will penetrate the skin
and on entry of the parasites in the skin, they will lose the tail
** second situation is typical for less favourable situations e.g. in winter: second generation redia to cercaria
enables more sufficient survival during winter
Note: for humans, infection occurs mainly due to eating contaminated vegetables/plants.