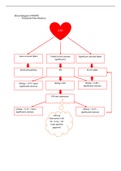
2.4.2 Injections and withdrawals
2.4.3 Equilibrium levels of real national output
2.4.4 The multiplier
- National income: total spending on goods and services
- Circular flow of income: money flows around the economy between
consumers/households and firms
- Output gap: measure of the difference between actual and potential growth/GDP
Withdrawals / Leakages
money flowing out of the circular flow of income
- saving
- imports
- taxation
- increase withdrawals = decreased national income
- a decrease in withdrawals increases the value of the multiplier
Injections
money flowing into the circular flow of income
- government spending
- exports
- investment
- increase injections = increased national income
- a decrease in injections decreases the value of the multiplier
- increase in mpc causes the value of the multiplier to rise
Multiplier & AD
measures the knock on effects when an injection or withdrawal changes
Injects of money from investment goes round the circular flow of income
- one person's spending is another person's income
- e,g construction workers will eat lunch in local cafes / stay in local hotels
Multiplier & unemployment
If unemployment falls:
- consumption & investment rises
- further rounds of increases in disposable income