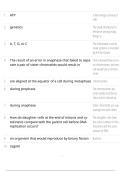
, Question 1
1.1 Definition of Operational Risk
Operational risk is generally defined as the potential for losses resulting from inadequate or
failed internal processes, people, systems, or from external events. The Basel Committee on
Banking Supervision (BCBS) provides one of the most authoritative definitions, stating that
operational risk is “the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes,
people and systems or from external events” (BCBS, 2011:3). This definition is deliberately
broad to capture both endogenous and exogenous factors that can disrupt organisational
stability.
Importantly, operational risk is distinct from market risk and credit risk, as it does not directly
relate to fluctuations in market prices or counterparty default but rather to the functioning of
the institution itself (Jorion, 2022:41). It can manifest in various forms, including fraud,
technology failures, natural disasters, regulatory breaches, and human error (Crouhy, Galai &
Mark, 2014:225).
From a corporate governance perspective, operational risk encompasses both strategic and
compliance dimensions, since operational failures can lead not only to financial losses but
also to reputational harm, legal penalties, and erosion of stakeholder trust (PwC, 2023). The
South African context also requires compliance with the King IV Report on Corporate
Governance, which emphasises that risk management should be integrated into
organisational culture and decision-making, making operational risk central to sustainable
value creation (IoDSA, 2016).
Thus, operational risk is best understood as a multidimensional construct that not only reflects
potential financial and non-financial losses but also embodies systemic vulnerabilities that
require proactive monitoring and control.
1.2 Draft Design for the Operational Risk Report
An operational risk report serves as a formal mechanism for identifying, assessing, monitoring,
and communicating the organisation’s exposure to operational risks. According to BCBS
(2011:23), an effective risk report should be timely, accurate, comprehensive, and tailored to
its audience (e.g., Board, management, regulators). A draft design could include the following
key components:
1.1 Definition of Operational Risk
Operational risk is generally defined as the potential for losses resulting from inadequate or
failed internal processes, people, systems, or from external events. The Basel Committee on
Banking Supervision (BCBS) provides one of the most authoritative definitions, stating that
operational risk is “the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes,
people and systems or from external events” (BCBS, 2011:3). This definition is deliberately
broad to capture both endogenous and exogenous factors that can disrupt organisational
stability.
Importantly, operational risk is distinct from market risk and credit risk, as it does not directly
relate to fluctuations in market prices or counterparty default but rather to the functioning of
the institution itself (Jorion, 2022:41). It can manifest in various forms, including fraud,
technology failures, natural disasters, regulatory breaches, and human error (Crouhy, Galai &
Mark, 2014:225).
From a corporate governance perspective, operational risk encompasses both strategic and
compliance dimensions, since operational failures can lead not only to financial losses but
also to reputational harm, legal penalties, and erosion of stakeholder trust (PwC, 2023). The
South African context also requires compliance with the King IV Report on Corporate
Governance, which emphasises that risk management should be integrated into
organisational culture and decision-making, making operational risk central to sustainable
value creation (IoDSA, 2016).
Thus, operational risk is best understood as a multidimensional construct that not only reflects
potential financial and non-financial losses but also embodies systemic vulnerabilities that
require proactive monitoring and control.
1.2 Draft Design for the Operational Risk Report
An operational risk report serves as a formal mechanism for identifying, assessing, monitoring,
and communicating the organisation’s exposure to operational risks. According to BCBS
(2011:23), an effective risk report should be timely, accurate, comprehensive, and tailored to
its audience (e.g., Board, management, regulators). A draft design could include the following
key components: