TOPIC 1
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
The heart and circulation exist to move substances around the body
Molecules move by diffusion in small, unicellular organisms because the distance is short, so it is fast enough to fulfil
the needs
Larger, complex, multicellular organisms rely on a mass transport system to move substances over the long distance by
mass flow (circulatory system in mammals)
- To carry raw materials from specialised exchange organs to body cells and to remove metabolic waste (carbon
dioxide)
- Blood provides nutrients and oxygen for cells in tissues and organs
Open circulatory system – blood circulates in open spaces and the substances diffuse between the blood and cells
Blood is enclosed in vessels in a closed circulatory system
- Higher blood pressures so blood travels faster and it is ore efficient
- Leaves heart -> arteries -> arterioles -> capillaries
- Venules -> veins -> heart
Animals with closed circulatory system are larger in size and more active than those with open systems
Single circulatory system – blood flows through the heart once for each complete circuit of the body
Double circulatory system – blood flows through the heart twice for each complete circuit of the body
- Right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs where it receives oxygen and oxygenated blood returns to
heart to be pumped to rest of the body by left ventricle
- 2nd pump gives a boost which makes the circulation of blood quicker, so they have a high metabolic rate as oxygen
and food substances needed for metabolic processes are delivered more quickly to cells
WATER
Good solvent – most biological reactions take place in solution and allows substances to be transported more easily
Structure
- Dipolar molecule – unevenly distributed electrical charge
- Shared negative hydrogen electrons pulled towards oxygen atom so hydrogen atoms have partial positive charge
and oxygen atom has partial negative charge
- Slightly negatively charged oxygen atoms attract slightly
positively charged hydrogen atoms of other water molecules
- Hydrogen bonds form between water molecules
- Slightly positive and negative ends attract other ions so they
become surrounded by water molecules and dissolve
Cohesive – attraction between water molecules because dipolar
- Helps water to flow which makes it good for transporting
substances
- Causes high surface tension
Some substances are hydrophobic and hydrophilic
- Hydrophobic substances e.g. lipids combine with proteins to form lipoproteins to transport in blood
High specific heat capacity so large input of energy causes small increase in temperature – warms and cools slowly
- Helps organisms maintain a steady body temperature
- High boiling point
THE HEART AND BLOOD VESSELS
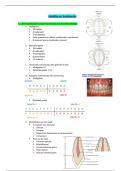
The heart
- Right side pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
- Left side pumps oxygenated blood to rest of the body
- Left and right sides are reverse on the diagram because it’s the left and right of the body
Heart dissection observations
- 4 main vessels attached; arteries are thick and rubbery and veins are thinner
- See left and right atria and ventricles and coronary arteries
- Left ventricle wall is thicker than the right
- Atria walls are thinner than ventricle walls
Left ventricle of the heart has thicker, more muscular walls than the right because it needs to contract more powerfully
to pump blood all around the body whereas the right side only needs to pump blood to the lungs which are nearby
, Ventricles have thicker, more muscular walls than atria because they need to pump blood out of the heart whilst atria
need to push the blood a short distance into the ventricles
AV valves link atria and ventricles and stop blood flowing back into atria when ventricles contract
- Cord attach the AV valves to ventricles to stop them being forced into the atria when the ventricles contract
SL valves link the ventricles to the pulmonary artery and aorta to stop blood flowing back into the heart after the
ventricles contract
Valves only open one way depending on the relative pressure of the heart chambers to ensure the flow of blood is in
one direction only
- Higher pressure behind a valve forces it open
- Higher pressure in front of a valve forces it shut
Collagen makes blood vessels strong and durable
Elastic fibres allow vessels to stretch and recoil
Smooth muscle cells in walls of vessels allow them to constrict and dilate
Arteries
- Carry blood from heart to rest of the body
- Narrow lumen
- More collagen and smooth muscle
- Thicker walled, muscular and have elastic tissue in walls to cope with high pressure
flow of blood
- Folded endothelium to allow it to expand and cope with high pressure flow of blood
- No valves
Veins
- Take blood back to the heart
- Wider lumen than arteries
- Thinner walls
- Less collagen and smooth muscle
- Valves to prevent backflow
- Less elastic tissue than arties because the blood is under lower pressure
- Contraction of skeletal muscles due to breathing or movement of limbs helps blood
flow through the veins
Capillaries
- Smallest
- Site of metabolic exchange – between cells and capillaries
- Networks of capillaries in tissue increase the surface area for exchange
- Walls are one cell thick which speeds up diffusion of substances into and out of cells
Each section of the artery stretches and recoils when blood flows through it
Blood flows more slowly in capillaries due to their narrow lumens which causes friction
between blood and capillary wall
- Allows gas exchange
The heart muscle is supplied with blood through its own coronary circulation; coronary arteries, network of capillaries
and 2 coronary veins
- Blood carries oxygen and glucose for aerobic respiration so the muscles have energy for contraction
Magnification
- Magnification = image size ÷ object size/actual size
- 1mm = 1000µm
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
The heart and circulation exist to move substances around the body
Molecules move by diffusion in small, unicellular organisms because the distance is short, so it is fast enough to fulfil
the needs
Larger, complex, multicellular organisms rely on a mass transport system to move substances over the long distance by
mass flow (circulatory system in mammals)
- To carry raw materials from specialised exchange organs to body cells and to remove metabolic waste (carbon
dioxide)
- Blood provides nutrients and oxygen for cells in tissues and organs
Open circulatory system – blood circulates in open spaces and the substances diffuse between the blood and cells
Blood is enclosed in vessels in a closed circulatory system
- Higher blood pressures so blood travels faster and it is ore efficient
- Leaves heart -> arteries -> arterioles -> capillaries
- Venules -> veins -> heart
Animals with closed circulatory system are larger in size and more active than those with open systems
Single circulatory system – blood flows through the heart once for each complete circuit of the body
Double circulatory system – blood flows through the heart twice for each complete circuit of the body
- Right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs where it receives oxygen and oxygenated blood returns to
heart to be pumped to rest of the body by left ventricle
- 2nd pump gives a boost which makes the circulation of blood quicker, so they have a high metabolic rate as oxygen
and food substances needed for metabolic processes are delivered more quickly to cells
WATER
Good solvent – most biological reactions take place in solution and allows substances to be transported more easily
Structure
- Dipolar molecule – unevenly distributed electrical charge
- Shared negative hydrogen electrons pulled towards oxygen atom so hydrogen atoms have partial positive charge
and oxygen atom has partial negative charge
- Slightly negatively charged oxygen atoms attract slightly
positively charged hydrogen atoms of other water molecules
- Hydrogen bonds form between water molecules
- Slightly positive and negative ends attract other ions so they
become surrounded by water molecules and dissolve
Cohesive – attraction between water molecules because dipolar
- Helps water to flow which makes it good for transporting
substances
- Causes high surface tension
Some substances are hydrophobic and hydrophilic
- Hydrophobic substances e.g. lipids combine with proteins to form lipoproteins to transport in blood
High specific heat capacity so large input of energy causes small increase in temperature – warms and cools slowly
- Helps organisms maintain a steady body temperature
- High boiling point
THE HEART AND BLOOD VESSELS
The heart
- Right side pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
- Left side pumps oxygenated blood to rest of the body
- Left and right sides are reverse on the diagram because it’s the left and right of the body
Heart dissection observations
- 4 main vessels attached; arteries are thick and rubbery and veins are thinner
- See left and right atria and ventricles and coronary arteries
- Left ventricle wall is thicker than the right
- Atria walls are thinner than ventricle walls
Left ventricle of the heart has thicker, more muscular walls than the right because it needs to contract more powerfully
to pump blood all around the body whereas the right side only needs to pump blood to the lungs which are nearby
, Ventricles have thicker, more muscular walls than atria because they need to pump blood out of the heart whilst atria
need to push the blood a short distance into the ventricles
AV valves link atria and ventricles and stop blood flowing back into atria when ventricles contract
- Cord attach the AV valves to ventricles to stop them being forced into the atria when the ventricles contract
SL valves link the ventricles to the pulmonary artery and aorta to stop blood flowing back into the heart after the
ventricles contract
Valves only open one way depending on the relative pressure of the heart chambers to ensure the flow of blood is in
one direction only
- Higher pressure behind a valve forces it open
- Higher pressure in front of a valve forces it shut
Collagen makes blood vessels strong and durable
Elastic fibres allow vessels to stretch and recoil
Smooth muscle cells in walls of vessels allow them to constrict and dilate
Arteries
- Carry blood from heart to rest of the body
- Narrow lumen
- More collagen and smooth muscle
- Thicker walled, muscular and have elastic tissue in walls to cope with high pressure
flow of blood
- Folded endothelium to allow it to expand and cope with high pressure flow of blood
- No valves
Veins
- Take blood back to the heart
- Wider lumen than arteries
- Thinner walls
- Less collagen and smooth muscle
- Valves to prevent backflow
- Less elastic tissue than arties because the blood is under lower pressure
- Contraction of skeletal muscles due to breathing or movement of limbs helps blood
flow through the veins
Capillaries
- Smallest
- Site of metabolic exchange – between cells and capillaries
- Networks of capillaries in tissue increase the surface area for exchange
- Walls are one cell thick which speeds up diffusion of substances into and out of cells
Each section of the artery stretches and recoils when blood flows through it
Blood flows more slowly in capillaries due to their narrow lumens which causes friction
between blood and capillary wall
- Allows gas exchange
The heart muscle is supplied with blood through its own coronary circulation; coronary arteries, network of capillaries
and 2 coronary veins
- Blood carries oxygen and glucose for aerobic respiration so the muscles have energy for contraction
Magnification
- Magnification = image size ÷ object size/actual size
- 1mm = 1000µm