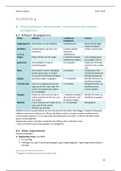
,QUESTION 1
Name and discuss how four (4) perceptual motor abilities are directly linked and have
an impact on academic learning. Complete your answer in the table below. (14)
Define the term perceptual motor (2 marks)
Perceptual motor development refers to the child’s ability to receive, interpret and respond
successfully to sensory information. Perceptual motor learning further involves the
implementation and refinement of sensory sensitivity to their world through movement by
mainly expanding the learner’s spatial and temporal world. (LSP1501 STUDY GUIDE, Page
117)
Name the perceptual ability (1 mark)
1. Spatial Orientation
Discuss how the ability is linked to learning and crucial in the movement programme (2
marks)
Spatial orientation enables children to comprehend their own physical position in space
relative to objects and peers. Mastering this ability allows them to correctly place letters on
lines, align numbers in math exercises, and maneuver through classroom environments
without colliding with others. Activities like navigating obstacle paths or playing directional
games foster spatial orientation, enhancing children’s confidence in organizing their work and
understanding positional concepts in literacy and numeracy(Department of Basic Education,
2011; Pienaar et al., 2011).
Name the perceptual ability (1 mark)
2. Laterality Awareness
, Discuss how the ability is linked to learning and crucial in the movement
programme (2 marks)
Laterality awareness refers to recognizing and consistently distinguishing the left and
right sides of one’s body, a foundation for directionality in reading and writing. Without
this skill, children may reverse letters or struggle to follow the left-to-right progression in
texts. Cross-lateral exercises, such as reaching across the body during gross motor
activities, reinforce laterality, promoting hand dominance, letter formation, and fluent
reading patterns vital for academic performance (Gallahue & Donnelly, 2007; Tomaz et
al., 2019).
Name the perceptual ability (1 mark)
3. Visual-Motor Coordination
Discuss how the ability is linked to learning and crucial in the movement
programme (2 marks)
Visual-motor coordination encompasses synchronizing visual perception with precise
physical actions, for instance, aligning the eyes and hands to cut shapes or copy
drawings. Strong visual-motor coordination underpins crucial classroom skills, including
writing, drawing, and manipulating learning tools. Incorporating games that involve
tossing and catching balls or tracing shapes during movement sessions significantly
Name and discuss how four (4) perceptual motor abilities are directly linked and have
an impact on academic learning. Complete your answer in the table below. (14)
Define the term perceptual motor (2 marks)
Perceptual motor development refers to the child’s ability to receive, interpret and respond
successfully to sensory information. Perceptual motor learning further involves the
implementation and refinement of sensory sensitivity to their world through movement by
mainly expanding the learner’s spatial and temporal world. (LSP1501 STUDY GUIDE, Page
117)
Name the perceptual ability (1 mark)
1. Spatial Orientation
Discuss how the ability is linked to learning and crucial in the movement programme (2
marks)
Spatial orientation enables children to comprehend their own physical position in space
relative to objects and peers. Mastering this ability allows them to correctly place letters on
lines, align numbers in math exercises, and maneuver through classroom environments
without colliding with others. Activities like navigating obstacle paths or playing directional
games foster spatial orientation, enhancing children’s confidence in organizing their work and
understanding positional concepts in literacy and numeracy(Department of Basic Education,
2011; Pienaar et al., 2011).
Name the perceptual ability (1 mark)
2. Laterality Awareness
, Discuss how the ability is linked to learning and crucial in the movement
programme (2 marks)
Laterality awareness refers to recognizing and consistently distinguishing the left and
right sides of one’s body, a foundation for directionality in reading and writing. Without
this skill, children may reverse letters or struggle to follow the left-to-right progression in
texts. Cross-lateral exercises, such as reaching across the body during gross motor
activities, reinforce laterality, promoting hand dominance, letter formation, and fluent
reading patterns vital for academic performance (Gallahue & Donnelly, 2007; Tomaz et
al., 2019).
Name the perceptual ability (1 mark)
3. Visual-Motor Coordination
Discuss how the ability is linked to learning and crucial in the movement
programme (2 marks)
Visual-motor coordination encompasses synchronizing visual perception with precise
physical actions, for instance, aligning the eyes and hands to cut shapes or copy
drawings. Strong visual-motor coordination underpins crucial classroom skills, including
writing, drawing, and manipulating learning tools. Incorporating games that involve
tossing and catching balls or tracing shapes during movement sessions significantly