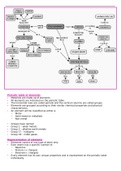
Physics Equations
Motion
!
• Average speed: 𝑠̅ = "
∆$
• Average velocity: 𝑣 = ∆"
!$
• Instantaneous velocity: 𝑣 = !"
%! &%"
• Average acceleration: 𝑎' = "
!%
• Instantaneous acceleration: 𝑎 = !"
Kinematic Equations
• 𝑣' = 𝑣( + 𝑎𝑡
• 𝑥' = 𝑥( + 𝑣̅ 𝑡
%! )%"
• 𝑣̅ = *
,
• 𝑥' = 𝑥( + 𝑣+ 𝑡 + * 𝑎𝑡 *
• 𝑣' * = 𝑣( * + 2𝑎(𝑥' − 𝑥( )
Unit Vectors
• 𝐴$ = 𝐴𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃
• 𝐴- = 𝐴𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
• 𝐴⃗ = 𝐴$ î + 𝐴$ ĵ + 𝐴$ k9
• Magnitude direction: 𝑅 = ;𝑅$ * + 𝑅- *
.
• Magnitude angle: 𝜃 = 𝑡𝑎𝑛&, <.#=
$
• Position: 𝑟⃑ = 𝑥î + 𝑦ĵ + 𝑧k9
Range
%" % (*0+121342)
• 𝑥= 6
%" % (134*2)
• If initial and final height are same: 𝑥 = 6
• If initial and final height are same: 𝑣! = 𝑣"# 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
• If angle is negative, it’s in 4th quad
o Add 90/180 to fix
Newton’s Laws
• Σ𝐹⃗ = 𝑚𝑎⃗
• 𝐹6 = 𝑚𝑔
• Pulley: 𝐹7 = 𝑚𝑔 − 𝐹8
• Vertical only: 𝐹 − 𝑚𝑔 = 𝑚𝑎
• Constant v = no net force = a=0
, • 1N = 1kgm/s2
Friction
• 𝑓1 ≤ 𝜇1 𝐹7
• 𝑓9 = 𝜇9 𝐹7
• 𝑤: = 𝑚𝑔𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃
• 𝑤" = 𝑚𝑔𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
• Incline: 𝑓$ = 𝑚𝑔𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 − 𝑚𝑎
• Incline: 𝑓$ = 𝜇$ 𝑚𝑔𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃
• Incline: 𝑎 = 𝑔𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
• Increase static friction by applying force upwards
Centripetal Force
&!
• |𝑎⃗% | =
%
'& !
• Tension: 𝑇 = 𝑚𝑎% = %
'& !
• 𝐹% = = 𝑚𝑎% = 𝐹( + 𝑚𝑔
%
&!
• No static friction: 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃 = %)
'& !
• Hill problem: 𝐹% = 𝑚𝑔 − 𝐹( = %
• 1 rev = 2𝜋R
• Constant radius & velocity tan to circle
• Acceleration towards center
Drag
• Linear drag: 𝐹⃗* = −𝑏𝑣⃗
• Quadratic drag: 6𝐹⃗* 6 = −𝑐𝑣 +
')
• Terminal velocity: 𝑣, =
-
' &"
• Time constant: 𝜏 = -
= )
• Time constant is time to reach v
• vt means air resistance = weight
Gravity
<=& (=% )
• 𝑔= >%
• G=6.67*10-11 Nm2/kg2
• Rearth=6.38*106 m
• Mearth=5.97*1024 kg
=6
• 𝐹6 = (> )?@"3"A!B)%
'()*+
<=C'()*+ =% %
• 𝐹> = >%
= >
<C'()*+
• 𝑣* = >
*D>
• Orbital velocity: 𝑣 =
"
Motion
!
• Average speed: 𝑠̅ = "
∆$
• Average velocity: 𝑣 = ∆"
!$
• Instantaneous velocity: 𝑣 = !"
%! &%"
• Average acceleration: 𝑎' = "
!%
• Instantaneous acceleration: 𝑎 = !"
Kinematic Equations
• 𝑣' = 𝑣( + 𝑎𝑡
• 𝑥' = 𝑥( + 𝑣̅ 𝑡
%! )%"
• 𝑣̅ = *
,
• 𝑥' = 𝑥( + 𝑣+ 𝑡 + * 𝑎𝑡 *
• 𝑣' * = 𝑣( * + 2𝑎(𝑥' − 𝑥( )
Unit Vectors
• 𝐴$ = 𝐴𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃
• 𝐴- = 𝐴𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
• 𝐴⃗ = 𝐴$ î + 𝐴$ ĵ + 𝐴$ k9
• Magnitude direction: 𝑅 = ;𝑅$ * + 𝑅- *
.
• Magnitude angle: 𝜃 = 𝑡𝑎𝑛&, <.#=
$
• Position: 𝑟⃑ = 𝑥î + 𝑦ĵ + 𝑧k9
Range
%" % (*0+121342)
• 𝑥= 6
%" % (134*2)
• If initial and final height are same: 𝑥 = 6
• If initial and final height are same: 𝑣! = 𝑣"# 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
• If angle is negative, it’s in 4th quad
o Add 90/180 to fix
Newton’s Laws
• Σ𝐹⃗ = 𝑚𝑎⃗
• 𝐹6 = 𝑚𝑔
• Pulley: 𝐹7 = 𝑚𝑔 − 𝐹8
• Vertical only: 𝐹 − 𝑚𝑔 = 𝑚𝑎
• Constant v = no net force = a=0
, • 1N = 1kgm/s2
Friction
• 𝑓1 ≤ 𝜇1 𝐹7
• 𝑓9 = 𝜇9 𝐹7
• 𝑤: = 𝑚𝑔𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃
• 𝑤" = 𝑚𝑔𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
• Incline: 𝑓$ = 𝑚𝑔𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 − 𝑚𝑎
• Incline: 𝑓$ = 𝜇$ 𝑚𝑔𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃
• Incline: 𝑎 = 𝑔𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
• Increase static friction by applying force upwards
Centripetal Force
&!
• |𝑎⃗% | =
%
'& !
• Tension: 𝑇 = 𝑚𝑎% = %
'& !
• 𝐹% = = 𝑚𝑎% = 𝐹( + 𝑚𝑔
%
&!
• No static friction: 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃 = %)
'& !
• Hill problem: 𝐹% = 𝑚𝑔 − 𝐹( = %
• 1 rev = 2𝜋R
• Constant radius & velocity tan to circle
• Acceleration towards center
Drag
• Linear drag: 𝐹⃗* = −𝑏𝑣⃗
• Quadratic drag: 6𝐹⃗* 6 = −𝑐𝑣 +
')
• Terminal velocity: 𝑣, =
-
' &"
• Time constant: 𝜏 = -
= )
• Time constant is time to reach v
• vt means air resistance = weight
Gravity
<=& (=% )
• 𝑔= >%
• G=6.67*10-11 Nm2/kg2
• Rearth=6.38*106 m
• Mearth=5.97*1024 kg
=6
• 𝐹6 = (> )?@"3"A!B)%
'()*+
<=C'()*+ =% %
• 𝐹> = >%
= >
<C'()*+
• 𝑣* = >
*D>
• Orbital velocity: 𝑣 =
"