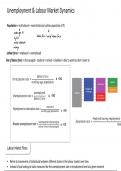
- The cytoskeleton is a network of fibres extending throughout the cytoplasm of the
cell.
- Responsible for:
o Organising the cell’s structure
o Organising the cell’s activities
o Anchoring many organelles
o Providing cell shape
o Aids motility (moving of the cell)
o Responds to environmental signals / stimuli
- The cytoskeleton is not rigid.
Components of the cytoskeleton:
- The cytoskeleton is made of three main components:
o Microtubules: thickest of the three components.
o Microfilaments: contains actin filaments and is the thinnest component.
o Intermediate filaments: fibres with diameters in the middle range.
- The assembly of polymers (monomers (single units) linked by chemical bonds) is
highly regulated by the cell according to the specific needs of the cell.
Roles of the cytoskeleton: support, motility and regulation
- Helps support the cell and maintain its shape.
- Interacts with the motor proteins to produce motility (location and movement of
parts).
, - Inside the cell, vesicles can travel along the monorails (Microtubules are complexes
of the protein, tubulin. They are the largest diameter of the cytoskeleton members
and serve as "monorails" along which organelles can move about) of the
cytoskeleton.
- Cytoskeleton may help regulate biochemical activities.
Microtubules:
- Hollow rods of about 25 nm in diameter and about 200 nm to 25 microns
(micrometres) long.
- The wall of each tube is made of a substance called tubulin – dimer (molecular
complex of chemicals that consists of a few repeating units consisting of two
monomers joined by a bond that can be either strong or weak, covalent or
intermolecular) of α-tubulin and β-tubulin.
200nm – 25 ųm
25nm
- Length can grow and shrink.
- The ends of the tubules are slightly different.
- The plus end can add or release dimers (see definition above) at a faster rate.
cell.
- Responsible for:
o Organising the cell’s structure
o Organising the cell’s activities
o Anchoring many organelles
o Providing cell shape
o Aids motility (moving of the cell)
o Responds to environmental signals / stimuli
- The cytoskeleton is not rigid.
Components of the cytoskeleton:
- The cytoskeleton is made of three main components:
o Microtubules: thickest of the three components.
o Microfilaments: contains actin filaments and is the thinnest component.
o Intermediate filaments: fibres with diameters in the middle range.
- The assembly of polymers (monomers (single units) linked by chemical bonds) is
highly regulated by the cell according to the specific needs of the cell.
Roles of the cytoskeleton: support, motility and regulation
- Helps support the cell and maintain its shape.
- Interacts with the motor proteins to produce motility (location and movement of
parts).
, - Inside the cell, vesicles can travel along the monorails (Microtubules are complexes
of the protein, tubulin. They are the largest diameter of the cytoskeleton members
and serve as "monorails" along which organelles can move about) of the
cytoskeleton.
- Cytoskeleton may help regulate biochemical activities.
Microtubules:
- Hollow rods of about 25 nm in diameter and about 200 nm to 25 microns
(micrometres) long.
- The wall of each tube is made of a substance called tubulin – dimer (molecular
complex of chemicals that consists of a few repeating units consisting of two
monomers joined by a bond that can be either strong or weak, covalent or
intermolecular) of α-tubulin and β-tubulin.
200nm – 25 ųm
25nm
- Length can grow and shrink.
- The ends of the tubules are slightly different.
- The plus end can add or release dimers (see definition above) at a faster rate.