Week 2: Lead Lessons
Photosynthesis II
Recap – chloroplast
Stacks of membranes = grana
Single granum – stacks of thylakoids (chlorophyll is found)
Covered in particles – responsible for ATP synthesis
Grana joined by lamella – act as skeleton and hold grana at good working distance
Stacks of membranes surrounded by stroma – contains enzymes needed to make final
glucose molecules
Light Independent Reactions
Calvin cycle
Doesn’t require light BUT REQUIRES PRODUCTS OF LDRs
Involves ENZYMES so is TEMP SENSITIVE
Series of enzyme catalysed reactions in cyclical pathway used to REDUCE CO2 TO
CARBOHYDRATE
Take place in STROMA – compartmentalising enzymes here
so conc is efficient and economical
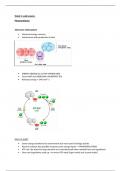
, LIR stages
1. CO2 from air combines with 5C compound (ribulose bisphosphate RuBP) in process
CARBON FIXATION
Requires enzyme RUBISCO (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase)
2. Forms HIGHLY UNSTABLE 6C compound – yet to be isolated and identified
3. Rapidly breaks into 2X 3C COMPOUND called GLYCERATE-3-PHOSPHATE (GP)
4. GP is REDUCED to form GLYERCALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE (GALP) => another 3C
compound
Requires HYDROGEN to be added to GP (comes from reduced NADP from LDR)
Requires ENERGY (hydrolysis of ATP from LDR)
5. Calvin cycle can take place day/night BUT STOPS IF REDUCED NADP AND ATP FROM LDRs
RUN OUT
Fate of GALP (3C)
Most used to regenerate 5C RuBP so cycle can continue
Some used to synthesise 6C glucose – GLUCONEOGENESIS
- Converted to disaccharide sucrose
- Polysaccharide starch
- Polysaccharide cellulose
Some used directly in cellular respiration
- Energy (ATP)
- Amino acids (nitrates from soil)
- Converted to acetyl co-enzyme A and used to synthesis fatty acids -> lipids/phospholipids
Photosynthesis II
Recap – chloroplast
Stacks of membranes = grana
Single granum – stacks of thylakoids (chlorophyll is found)
Covered in particles – responsible for ATP synthesis
Grana joined by lamella – act as skeleton and hold grana at good working distance
Stacks of membranes surrounded by stroma – contains enzymes needed to make final
glucose molecules
Light Independent Reactions
Calvin cycle
Doesn’t require light BUT REQUIRES PRODUCTS OF LDRs
Involves ENZYMES so is TEMP SENSITIVE
Series of enzyme catalysed reactions in cyclical pathway used to REDUCE CO2 TO
CARBOHYDRATE
Take place in STROMA – compartmentalising enzymes here
so conc is efficient and economical
, LIR stages
1. CO2 from air combines with 5C compound (ribulose bisphosphate RuBP) in process
CARBON FIXATION
Requires enzyme RUBISCO (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase)
2. Forms HIGHLY UNSTABLE 6C compound – yet to be isolated and identified
3. Rapidly breaks into 2X 3C COMPOUND called GLYCERATE-3-PHOSPHATE (GP)
4. GP is REDUCED to form GLYERCALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE (GALP) => another 3C
compound
Requires HYDROGEN to be added to GP (comes from reduced NADP from LDR)
Requires ENERGY (hydrolysis of ATP from LDR)
5. Calvin cycle can take place day/night BUT STOPS IF REDUCED NADP AND ATP FROM LDRs
RUN OUT
Fate of GALP (3C)
Most used to regenerate 5C RuBP so cycle can continue
Some used to synthesise 6C glucose – GLUCONEOGENESIS
- Converted to disaccharide sucrose
- Polysaccharide starch
- Polysaccharide cellulose
Some used directly in cellular respiration
- Energy (ATP)
- Amino acids (nitrates from soil)
- Converted to acetyl co-enzyme A and used to synthesis fatty acids -> lipids/phospholipids