Chapter 24
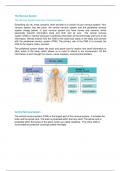
1. Know the organs of the digestive system (Figure 24-1). Know which are major organs
and which are accessory organs.
2. Know about the functions and processes of the digestive system: ingestion, mechanical
digestion and propulsion, chemical digestion, secretion, absorption, and defecation.
3. Know about mesenteries. Which organs are retroperitoneal?
4. Know the histology of the digestive tract… mostly the type of epithelia in the mucosa,
and features that distinguish the different organs of the digestive tract, i.e., 3 layers of
muscle in stomach, Peyer’s patches, etc. Also, know the different types of cells and their
products, i.e., parietal cells of stomach produce HCl and Intrinsic Factor, etc. Know the
layers of smooth muscle in the digestive tract, such as inner layer is circular and outer
layer is longitudinal. Also know about the two neural plexuses: submucosal neural
plexus and myenteric plexus.
5. Understand how motility of the digestive tract works: peristalsis and segmentation.
6. Mouth: know the number of teeth in adults and children. Include how many are incisors,
how many are canines, how many are premolar and how many are molar teeth. Know
which ones are deciduous teeth (also known as primary teeth, milk teeth, or baby teeth),
and which ones are permanent teeth.
7. Know how many salivary glands we have. Know their type of secretion, for example,
pure serous secretion, pure mucus secretion, and mixed secretion. Know the enzyme in
saliva. What salivary amylase breaks.
8. Pharynx: understand the mechanism of swallowing.
9. Esophagus: know the histology of esophagus, and the different types of muscle forming
the upper, middle, and lower thirds of the esophagus.
10. Stomach: know the different regions of the stomach.
11. Know the histology of stomach and their muscle layers.
12. Know how the gastric pits are made. Know the products of gastric cells: parietal cells,
chief cells, enteroendocrine cells.
13. Understand the mechanism of chemical and mechanical digestion. Know the regulation
of gastric activity (phases of digestion – understand the Spotlight of Figure 24-15,
including the Central Reflexes).
14. Pancreas: know the anatomy and histology of pancreas. Know the pancreatic secretions.
Know what type of pancreatic secretion these two duodenal hormones cause:
cholecystokinin (CCK) and secretin. Know what the different digestive enzymes
produced by the pancreas are, and what these breaks down.
15. Liver: know the gross anatomy of the liver, such as the four hepatic lobes, the ligaments,
the cell types (hepatocytes and Kupffer cells – Stellate macrophages), and the
Page 1 of 5
, BIOL 2402 STUDY GUIDE Summer 2024
components of the portal triad. Know about the Hepatic Portal System and the Bile Duct
System.
16. Know the metabolic activities of the liver: carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism,
amino acid metabolism, water removal, vitamin storage, mineral storage, and drug
inactivation.
17. Know the hematological regulation of the liver: phagocytosis, antigen presentation,
synthesis of plasma proteins, removal of circulating hormones, removal of antibodies,
removal and/or storage of toxins.
18. Know about production and function of bile.
19. Small intestine: know the segments of the small intestine: duodenum, jejunum, and
ileum. Know how to distinguish them histologically. Know what are the following and
where these are found: circular folds, intestinal villi, brush border, lacteal, duodenal
submucosal glands (also known as Brunner’s glands), intestinal crypts, Paneth cells, and
Peyer’s patches. Know the effects of gastrin, secretin and CCK (understand Figure 24-
23).
20. Large intestine: know the segments of the large intestine (cecum, colon, and rectum). In
the cecum, the appendix is found. Know the segments further subdividing the colon:
ascending colon, right hepatic flexure, transverse colon, left splenic flexure, descending
colon, and sigmoid colon.
21. Rectum: know the internal and external anal sphincters.
22. Also know the histology of the colon; include knowing about hemorrhoids. What is the
function of so many goblet cells?
23. Understand the defecation reflex (Figure 24-26).
24. Know where each nutrient began to be digested. See Spotlight for figure 24-27.
Chapter 26
1. Know the anatomy of the urinary system: organs of the urinary system (Figure 26-1),
position and related structures of the kidneys (Figure 26-2), and the gross anatomy of the
urinary system (Figure 26-3).
2. Know the internal structure of kidneys (Figure 26-4): renal sinus, renal cortex, renal
medulla, renal pyramids, renal columns, kidney lobes, renal papilla, major calyces, minor
calyces, renal pelvis, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra.
3. Know the blood supply to kidneys in order (Figure 26-5): renal artery, segmental arteries,
interlobar arteries, arcuate arteries, cortical radial arteries, afferent arterioles, glomerulus,
efferent arterioles, peritubular capillaries, vasa recta, venule, cortical radial vein, arcuate
vein, interlobar vein, and renal vein.
Page 2 of 5