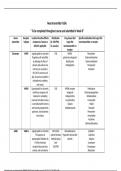
Modern society:
Modern society emerged in western europe in the late 18th century. Characteristics of it include:
- Nation state - key political unit in modern society. Rules territory as a powerful centralised
state. Created institutions such as education, welfare and legal institutions to regulate
lives of citizens
- Capitalism - modern society is based on private ownership of means of production and
exploiting labour of workers
- Rationality science and technology- science has become important in medicines and
technology in communications.
- Individualism - personal freedom hold profound importance as collectivism, tradition and
culture lose their importance
Globalisation:
The increased interconnectedness between countries.
1. TECHNOLOGICAL CHANGES: the world has become interconnected through technological
changes. Information can be exchanged within seconds with a click, internet and satellite
communicated has created time-space compression closing the distance between people
However it does bring some risks. Beck argues we live in a ‘risk society’ meaning that
threats are increasingly coming from human made technology.
2. ECONOMIC CHANGES - The global economy is becoming more electronic, focusing on creating and
sharing information like music, TV shows, and data processing through global electronic networks.
In this electronic economy, money is always moving, with 24-hour global transactions
allowing instant fund transfers for profit, creating a "risk society." Another key factor in
globalisation is trans-national companies (TNCs), which operate all over the world and
manage production globally.
Transnational companies (TNCs) are businesses that operate in multiple countries. They
have headquarters in one country but have branches, factories, or offices in others. FOR
EXAMPLE, Apple, Coca Cola.
3. POLITICAL CHANGES - big companies and consumers have more control over the economy that
the government or the state has. As a result, the government finds it harder to regulate and police
large companies. Lash and Urry call this ‘Disorganised Capitalism’ - traditional ways of controlling
companies is no longer effective
4. CHANGES IN CULTURE AND IDENTITY:
Globalisation makes it difficult for cultures to stay separate due to technology and mass
media. We now live in a global culture where Western media spreads Western ideas
everywhere. Companies like Nike also help by selling the same products in many
countries, making people's tastes more similar.
Postmodernism
It has been a movement since the 1970s. Post modernity states that our global village is becoming
unstable, media saturated where image and reality are inseparable. We can differ between what is
reality and what is fake.
Foucault argues there is no absolute truth of knowledge. There is no objective criteria that we can use
to establish if a theory is true or not. He argues if we can't make sure scientific knowledge is true or
correct we can't use it to improve society. He argues theories are meta narratives with only one
person's view of reality.