General Note
Tuesday, 23 January 2024 12:19 PM
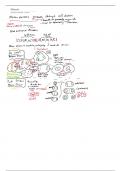
(Pro Vs Eu) Karyotic Cells
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus, Eukaryotes do.
Examples of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes are Bacteria (Pro), Animal or Plant cells (Eu), Fungi (Eu), Protists like Amoeba (Eu).
Cell Theory (Cells are the smallest building block of life, Cells can only be made through other cells/mitosis, All living things are made of
cells, which is why viruses aren't living)
The parts of the cells are called organelles (eg. Nuclei, Ribosomes, Mitochondria)
Each organelle has a purpose, eg. Mitochondria makes ATP energy from glucose, which then is used to power other biological proteins
Endoplasmic Reticulum packages proteins
Ribosomes make protein
Nuclei hold the DNA
Plant's Chloroplast - photosynthesis
Golgi Apparatus - Packages proteins in vesicles
DNA
DNA has a double helix structure composed of a sugar-phosphate backbone and complementary base pairs.
Most genes code for the production of protein, for the function of RNA molecules (like transfer RNA), regulating the expression for other
genes (making genes make more protein, or supress their ability).
The full term is Deoxyribonucleic acid. Ensure to use this during an exam BEFORE the abbreviation (DNA)
Holds instructions for the proteins in our body
Every cell (with a few exceptions) has every instruction for that organism.
There are 46 chromosomes in every cell. 20-35 000 genes in each cell
Red blood cells do not have DNA. (Their purpose is to carry oxygen around the body via Haemoglobin, and Co2 back to your lungs)
They just have "stacks of Haemoglobin"
DNA is otherwise located in the nucleus (Eukaryotic, Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus)
DNA is unique to everyone (small mutations make everyone different)
Exemption being identical twins (maternal twins/ Dizygotic twins)
Zygole is the cell formed when sperm fertilises an egg. When about 8 cells are developed they can split, creating two identical things,
which have the same DNA.
The result of this is identical twins who will look the same, unless there are environmental factors.
Nucleus has chromosomes which are long stretches of DNA.
Structure of DNA
Nucleotides consist of Phosphate groups, which has phosphates, attached to a pentose sugar (comprised of a deoxyribose, a 5 C sugar),
and a nitrogenous base (They are the bases). These are then linked via covalent bonds to other Phosphate Groups
Phosphate group
Covalent Bonds
Nitrogenous Base
, Complementary Base Pairing
A T G or C
Apples in the Tree, Cars in the Garage
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
Hydrogen Bonding
O has a higher electronegativity, than H. Therefore O takes a greater share of electrons. Due to uneven sharing of electrons, O is slightly
negative, and H is slightly positive. This makes H20 a polar molecule. Covalent bonds has an intermolecular bond, much stronger than a
Hydrogen bond, which is between different molecules. There are hydrogen bonds between the base pairs.
Hydrogen bonds are between the bases in the m
Hydrogen bonds are able to separate during transcription, useful for copying (DNA to RNA) and replication (DNA to DNA). Weak, non
covalent. Oxygen is slightly negative, Hydrogen is slightly positive. Dash lines represent hydrogen bonds.
DNA consists of long strands of nucleotides connected by these bonds, called polynucleotides.
It is also important to remember that DNA is double stranded.
Complimentary Base Pairing Pt. 2
ATGCAATTACGGATCATTATCGAATCTTA
TACGTTAATGCCTAGTAATAGCTTAGAAT
TTAGT
AATCA
GCTAG
CGATC
TAGCCGTATACGATGACT
ATCGGCATATGCTACTGA
DNA Recap
Located on chromo
Grouped into genes
Genes have sequences of DNA
Grouped into 3s called triplets (the sequences)
Each 3 bases code for one amino acid.
TAG codes for one amino acid (TGC, AGT etc.)
These proteins have roles/jobs in the body.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
A process used to make copies or amplify fragments of DNA from even minuscule samples
One of the advantages is speed
The most important part of PCR is DNA polymerase (enzyme)
It makes DNA polymers
STEPS:
1. Denature DNA (raise the temp to separate strands, breaking the bonds between the bases (94 degrees))
Tuesday, 23 January 2024 12:19 PM
(Pro Vs Eu) Karyotic Cells
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus, Eukaryotes do.
Examples of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes are Bacteria (Pro), Animal or Plant cells (Eu), Fungi (Eu), Protists like Amoeba (Eu).
Cell Theory (Cells are the smallest building block of life, Cells can only be made through other cells/mitosis, All living things are made of
cells, which is why viruses aren't living)
The parts of the cells are called organelles (eg. Nuclei, Ribosomes, Mitochondria)
Each organelle has a purpose, eg. Mitochondria makes ATP energy from glucose, which then is used to power other biological proteins
Endoplasmic Reticulum packages proteins
Ribosomes make protein
Nuclei hold the DNA
Plant's Chloroplast - photosynthesis
Golgi Apparatus - Packages proteins in vesicles
DNA
DNA has a double helix structure composed of a sugar-phosphate backbone and complementary base pairs.
Most genes code for the production of protein, for the function of RNA molecules (like transfer RNA), regulating the expression for other
genes (making genes make more protein, or supress their ability).
The full term is Deoxyribonucleic acid. Ensure to use this during an exam BEFORE the abbreviation (DNA)
Holds instructions for the proteins in our body
Every cell (with a few exceptions) has every instruction for that organism.
There are 46 chromosomes in every cell. 20-35 000 genes in each cell
Red blood cells do not have DNA. (Their purpose is to carry oxygen around the body via Haemoglobin, and Co2 back to your lungs)
They just have "stacks of Haemoglobin"
DNA is otherwise located in the nucleus (Eukaryotic, Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus)
DNA is unique to everyone (small mutations make everyone different)
Exemption being identical twins (maternal twins/ Dizygotic twins)
Zygole is the cell formed when sperm fertilises an egg. When about 8 cells are developed they can split, creating two identical things,
which have the same DNA.
The result of this is identical twins who will look the same, unless there are environmental factors.
Nucleus has chromosomes which are long stretches of DNA.
Structure of DNA
Nucleotides consist of Phosphate groups, which has phosphates, attached to a pentose sugar (comprised of a deoxyribose, a 5 C sugar),
and a nitrogenous base (They are the bases). These are then linked via covalent bonds to other Phosphate Groups
Phosphate group
Covalent Bonds
Nitrogenous Base
, Complementary Base Pairing
A T G or C
Apples in the Tree, Cars in the Garage
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
Hydrogen Bonding
O has a higher electronegativity, than H. Therefore O takes a greater share of electrons. Due to uneven sharing of electrons, O is slightly
negative, and H is slightly positive. This makes H20 a polar molecule. Covalent bonds has an intermolecular bond, much stronger than a
Hydrogen bond, which is between different molecules. There are hydrogen bonds between the base pairs.
Hydrogen bonds are between the bases in the m
Hydrogen bonds are able to separate during transcription, useful for copying (DNA to RNA) and replication (DNA to DNA). Weak, non
covalent. Oxygen is slightly negative, Hydrogen is slightly positive. Dash lines represent hydrogen bonds.
DNA consists of long strands of nucleotides connected by these bonds, called polynucleotides.
It is also important to remember that DNA is double stranded.
Complimentary Base Pairing Pt. 2
ATGCAATTACGGATCATTATCGAATCTTA
TACGTTAATGCCTAGTAATAGCTTAGAAT
TTAGT
AATCA
GCTAG
CGATC
TAGCCGTATACGATGACT
ATCGGCATATGCTACTGA
DNA Recap
Located on chromo
Grouped into genes
Genes have sequences of DNA
Grouped into 3s called triplets (the sequences)
Each 3 bases code for one amino acid.
TAG codes for one amino acid (TGC, AGT etc.)
These proteins have roles/jobs in the body.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
A process used to make copies or amplify fragments of DNA from even minuscule samples
One of the advantages is speed
The most important part of PCR is DNA polymerase (enzyme)
It makes DNA polymers
STEPS:
1. Denature DNA (raise the temp to separate strands, breaking the bonds between the bases (94 degrees))