Positioning & Surfaces
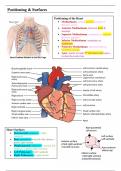
Positioning of the Heart
• Mediastinum: central/midline portion of
thoracic cavity
• Anterior Mediastinum: between heart &
sternum
• Superior Mediastinum: terminates at superior
thoracic aperture
• Inferior Mediastinum: terminates at
diaphragm
• Posterior Mediastinum: between heart &
vertebral column
• Apex: points towards 5th left intercostal space
in mid-clavicular line
Heart Surfaces
• Sternocostal (anterior) = right
ventricle
• Base (posterior) = mostly left atrium +
partly right atrium
• Diaphragmatic (inferior) = mostly left
ventricle + partly right ventricle
• Left Pulmonary = left ventricle
• Right Pulmonary = right atrium
, Pericardium
Pericardium
• Double-layered membrane surrounding heart
• Fibrous Pericardium: tough, elastic, external layer connected to sternum by
sternopericardial ligament
• Serous Pericardium: thin, inner layer, divided into 2 layers
o Parietal Layer (outer): fused to fibrous pericardium
o Visceral Layer (inner): attached to heart surface (forms epicardium)
• Attached to diaphragm, sternum & outer layer of great vessels
• Prevents heart from increasing in size too rapidly
Pericardial Cavity
• Between parietal & visceral
layers of serous pericardium
• Contains lubricating serous
fluid, which minimises
friction
Pericardial Sinuses
• Transverse Sinus: between
aorta / pulmonary artery /
vena cava
• Oblique Sinus: posterior,
behind left atrium
Positioning of the Heart
• Mediastinum: central/midline portion of
thoracic cavity
• Anterior Mediastinum: between heart &
sternum
• Superior Mediastinum: terminates at superior
thoracic aperture
• Inferior Mediastinum: terminates at
diaphragm
• Posterior Mediastinum: between heart &
vertebral column
• Apex: points towards 5th left intercostal space
in mid-clavicular line
Heart Surfaces
• Sternocostal (anterior) = right
ventricle
• Base (posterior) = mostly left atrium +
partly right atrium
• Diaphragmatic (inferior) = mostly left
ventricle + partly right ventricle
• Left Pulmonary = left ventricle
• Right Pulmonary = right atrium
, Pericardium
Pericardium
• Double-layered membrane surrounding heart
• Fibrous Pericardium: tough, elastic, external layer connected to sternum by
sternopericardial ligament
• Serous Pericardium: thin, inner layer, divided into 2 layers
o Parietal Layer (outer): fused to fibrous pericardium
o Visceral Layer (inner): attached to heart surface (forms epicardium)
• Attached to diaphragm, sternum & outer layer of great vessels
• Prevents heart from increasing in size too rapidly
Pericardial Cavity
• Between parietal & visceral
layers of serous pericardium
• Contains lubricating serous
fluid, which minimises
friction
Pericardial Sinuses
• Transverse Sinus: between
aorta / pulmonary artery /
vena cava
• Oblique Sinus: posterior,
behind left atrium