Apuntes
, Resumen
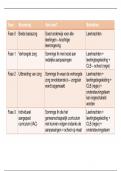
Scales of measurement:
1) Nominal: can’t be ordered, numbers are just names/tags
-> Valid operations: membership and equivalence
Job titles
2) Ordinal —> can be ordered but spaces between 2nd and 3rd don’t have to be the same
-> Valid operations: membership, equivalence and order
Grades in an exam
3) Interval —> can be ordered, spaces from one unit to the next are the same, but 0 doesn’t mean “the
lack” of something
-> Valid operations: membership, equivalence, order and addition / subtraction
Temperature
4) Ratio —> can be ordered, spaces are equally spaced and 0 means lack of the property
-> Valid operations: membership, equivalence, order, addition / subtraction and multiplication / division
Types of (statistical varibale)
Qualitative variables: Categories can’t be ordered, numbers simply serve as a tag to name the category
-> nominal scale
Quasi-quantitative variables: Categories can be rank-ordered but are not equally spaced
-> ordinal scale
Quantitative variables: Categories always satisfy the properties of magnitude and intervals (sometimes
absolute zero)
-> interval and ratio scale
• Discrete variables: Consist of separate, isolated categories. No values can exist between two
neighbouring categories (they can only take on a finite or countably infinite number of values)
• Continuous variables: There are an infinite number of possible values that fall between any two
chosen categories (they can take on an uncountably infinite number of values)
, Resumen
Scales of measurement:
1) Nominal: can’t be ordered, numbers are just names/tags
-> Valid operations: membership and equivalence
Job titles
2) Ordinal —> can be ordered but spaces between 2nd and 3rd don’t have to be the same
-> Valid operations: membership, equivalence and order
Grades in an exam
3) Interval —> can be ordered, spaces from one unit to the next are the same, but 0 doesn’t mean “the
lack” of something
-> Valid operations: membership, equivalence, order and addition / subtraction
Temperature
4) Ratio —> can be ordered, spaces are equally spaced and 0 means lack of the property
-> Valid operations: membership, equivalence, order, addition / subtraction and multiplication / division
Types of (statistical varibale)
Qualitative variables: Categories can’t be ordered, numbers simply serve as a tag to name the category
-> nominal scale
Quasi-quantitative variables: Categories can be rank-ordered but are not equally spaced
-> ordinal scale
Quantitative variables: Categories always satisfy the properties of magnitude and intervals (sometimes
absolute zero)
-> interval and ratio scale
• Discrete variables: Consist of separate, isolated categories. No values can exist between two
neighbouring categories (they can only take on a finite or countably infinite number of values)
• Continuous variables: There are an infinite number of possible values that fall between any two
chosen categories (they can take on an uncountably infinite number of values)