Topic 7: Run for your Life
Muscle Contraction
Skeletal Muscle
There are different types of muscle - for example, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and cardiac
muscle. Skeletal muscle is the type of muscle used for physical movement such as when we pick up
objects or go for a run. Skeletal muscle is attached to bone through tendons and it contracts or
relaxes in order to move the bone that it is connected to. Muscles can work in antagonistic pairs so
that when one muscle contracts, the other relaxes.
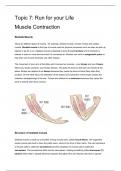
The movement of your arm at the elbow joint involves two muscles - your biceps and your triceps.
When your bicep contracts, your triceps relaxes. This pulls the bone so that your arm bends at the
elbow. Biceps are referred to as flexors because they cause the bone to bend (flex) when they
contract. On the other hand, the relaxation of the biceps and contraction of the triceps causes the
extension (straightening) of the arm. Triceps are referred to as extensors because they cause the
bond to extend when they contract.
Structure of skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle is made up of bundles of long muscle cells, called muscle fibres. The organelles
inside muscle cells tend to have the prefix sarco- stuck to the front of their name. The cell membrane
of muscle cells is called the sarcolemma and the cytoplasm of muscle cells is called the
sarcoplasm. The sarcolemma folds into the sarcoplasm, creating something called transverse (T)
tubules which help to spread electrical impulses throughout the cell. Muscle cells have a special
, organelle called the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which stores calcium ions for muscle contraction.
Muscle cells also differ from other cells in that they contain many nuclei (they are multinucleate) and
lots of mitochondria to generate ATP for muscle contraction. In addition, muscle fibres contain long
cylinders of protein called myofibrils, which enable the muscle fibre to contract.
Sarcomeres
Myofibrils are made up of many short units called sarcomeres, which are made up of two types of
myofilament: myosin and actin.
• Myosin is a thick myofilament and appears as a dark band (called the A band) under the
microscope.
• Actin is a thin myofilament and appears as a light band (called the I band) under the
microscope.
• At the end of each sarcomere is a Z-line. Sarcomeres are joined together lengthways at the
Z-line.
• Right in the middle of the sarcomere is a region called the M-line.
• The H-zone refers to the portion of the A-band which only contains myosin filaments (and not
the portions where actin overlaps with myosin).
Sliding Filament Theory
When muscle fibres contract, the myosin and actin myofilaments move closer together by sliding
over one another. This makes the sarcomere shorter and they contract. Remember that the actin
and myosin myofilaments themselves don’t contract - they always stay the same length. As the
Muscle Contraction
Skeletal Muscle
There are different types of muscle - for example, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and cardiac
muscle. Skeletal muscle is the type of muscle used for physical movement such as when we pick up
objects or go for a run. Skeletal muscle is attached to bone through tendons and it contracts or
relaxes in order to move the bone that it is connected to. Muscles can work in antagonistic pairs so
that when one muscle contracts, the other relaxes.
The movement of your arm at the elbow joint involves two muscles - your biceps and your triceps.
When your bicep contracts, your triceps relaxes. This pulls the bone so that your arm bends at the
elbow. Biceps are referred to as flexors because they cause the bone to bend (flex) when they
contract. On the other hand, the relaxation of the biceps and contraction of the triceps causes the
extension (straightening) of the arm. Triceps are referred to as extensors because they cause the
bond to extend when they contract.
Structure of skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle is made up of bundles of long muscle cells, called muscle fibres. The organelles
inside muscle cells tend to have the prefix sarco- stuck to the front of their name. The cell membrane
of muscle cells is called the sarcolemma and the cytoplasm of muscle cells is called the
sarcoplasm. The sarcolemma folds into the sarcoplasm, creating something called transverse (T)
tubules which help to spread electrical impulses throughout the cell. Muscle cells have a special
, organelle called the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which stores calcium ions for muscle contraction.
Muscle cells also differ from other cells in that they contain many nuclei (they are multinucleate) and
lots of mitochondria to generate ATP for muscle contraction. In addition, muscle fibres contain long
cylinders of protein called myofibrils, which enable the muscle fibre to contract.
Sarcomeres
Myofibrils are made up of many short units called sarcomeres, which are made up of two types of
myofilament: myosin and actin.
• Myosin is a thick myofilament and appears as a dark band (called the A band) under the
microscope.
• Actin is a thin myofilament and appears as a light band (called the I band) under the
microscope.
• At the end of each sarcomere is a Z-line. Sarcomeres are joined together lengthways at the
Z-line.
• Right in the middle of the sarcomere is a region called the M-line.
• The H-zone refers to the portion of the A-band which only contains myosin filaments (and not
the portions where actin overlaps with myosin).
Sliding Filament Theory
When muscle fibres contract, the myosin and actin myofilaments move closer together by sliding
over one another. This makes the sarcomere shorter and they contract. Remember that the actin
and myosin myofilaments themselves don’t contract - they always stay the same length. As the