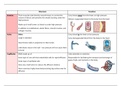
Data Analysis
Cases: The objects described by a set of data, customers
Variable: A characteristic of a case, profit
Distribution of a variable: the values the variable takes and how often it takes them
Quantitative Variable: Takes numerical values for which we can do arithmetic, age
histograms, stemplots, time plots
Categorical Variable: Places a case into one of several groups or categories, own home
bar graphs and pie charts
Bar graphs: Each category is represented by a bar.
Pie charts; the slices must represent the parts of one whole
Histograms and stemplots: These are summary graphs for a single variable. They are very
useful to understand the pattern of variability in the data.
- Histograms; The range of values that a variable can take is divided into equal size
intervals. The histogram shows the number of individual data points that fall in each
interval.
shape, center, and spread. symmetric, skewed left, skewed right, two peakz, outlier
- stemplot, quantitative data, small data quick and easy, can see the data values
outliers: observations that lie outside the overall pattern of a distribution
Line graphs: time plots. Use when there is a meaningful sequence, like time. The line
connecting the points helps emphasize any change over time. x-as time. scales matter
trend: a rise or fall that persists over time
seasonal variation: A pattern that repeats itself at regular intervals of time
mean; average, center of mass
median is midpoint of distribution, half are smaller and half larger
even: n/2 odd (n+1)/2
mean and median only same if distribution is symmetrical. median is resistant to outliers
percentiles:what data value has a certain percent of the data at or below it
quartiles: 1 quartile 25%, third quartile 75%
5 number summary: largest, third quartile, median, first quartile, lowest. min Q1 M Q3 max
boxplot
interquartile range: difference between quartiles 1 and 3, for outliers
suspected outliers: outliers more than 1,5 times the size of IQR
standard deviation s: variation around the mean
not resistant to outliers
has te same units of measurement as the original observations
Cases: The objects described by a set of data, customers
Variable: A characteristic of a case, profit
Distribution of a variable: the values the variable takes and how often it takes them
Quantitative Variable: Takes numerical values for which we can do arithmetic, age
histograms, stemplots, time plots
Categorical Variable: Places a case into one of several groups or categories, own home
bar graphs and pie charts
Bar graphs: Each category is represented by a bar.
Pie charts; the slices must represent the parts of one whole
Histograms and stemplots: These are summary graphs for a single variable. They are very
useful to understand the pattern of variability in the data.
- Histograms; The range of values that a variable can take is divided into equal size
intervals. The histogram shows the number of individual data points that fall in each
interval.
shape, center, and spread. symmetric, skewed left, skewed right, two peakz, outlier
- stemplot, quantitative data, small data quick and easy, can see the data values
outliers: observations that lie outside the overall pattern of a distribution
Line graphs: time plots. Use when there is a meaningful sequence, like time. The line
connecting the points helps emphasize any change over time. x-as time. scales matter
trend: a rise or fall that persists over time
seasonal variation: A pattern that repeats itself at regular intervals of time
mean; average, center of mass
median is midpoint of distribution, half are smaller and half larger
even: n/2 odd (n+1)/2
mean and median only same if distribution is symmetrical. median is resistant to outliers
percentiles:what data value has a certain percent of the data at or below it
quartiles: 1 quartile 25%, third quartile 75%
5 number summary: largest, third quartile, median, first quartile, lowest. min Q1 M Q3 max
boxplot
interquartile range: difference between quartiles 1 and 3, for outliers
suspected outliers: outliers more than 1,5 times the size of IQR
standard deviation s: variation around the mean
not resistant to outliers
has te same units of measurement as the original observations