RESPIRATION MELABOLISM
- &
> the su
-
-
mac ,
releaseenergy during the oxidation f organic
body
,
nn
- ~ PLANTS molecules
↳ exothermic reaction
.
ENZYMEACTION &
- AEROBIC ↳ releases
energy to
on
ANAERABIC (without 02) surroundingSe
complexe
respiration
respiration
carbon-water
f
>
-
glucose + o ygen
-
PAN dioxide
+s
2 MakingCellulose enzyme ~
Cott 206 + 602-6CO2 GHz0
YEASx
+
S
+
for use in cell walls shape to enzyme's
active site
supportive
-
used in ↳ strong +
glucose-
lactic d bread making
I
acid
glucose- > ethanol dioxide
+
carbon
& ↑ -
builds up I
t↓
Respiration
,
in musches : aicono 1
is browdown LUCOSE
3 Making Amino Acide
nitrate ions areadded to
causes usecivindustry glucose
onygendebt (winemaking& to release energy glucose to make amino acids
↳ aerobic respiration for protein synthesis
-
↳ the volume
of oxygen required to
neutralise the lactic acid produced Making starch
E -
5 4 Making Lipide/Fats FACTOR
during anaerobic respiration molecules can be
glucose glucose converted into lipid
linked together forming a
for storage (in seeds/nuts)
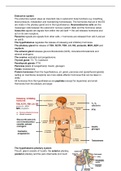
1HEARTRATET
3 BREATH VOLUME
insoluble starch for storage CA
↑ amount air in each
1
&
lungs ↳
into
breath goes an
8
D
to deliver Cott20s up
and O2 to changes during expand more ;
EXERCISE
/ Of diffuser
=
-
1 more ↳
respiring cells ;
&
waste products the blood
removed quickly d
2 BREATHING RATE
PHOTOSUNTHESIS -
> chemical in which plants 2
process
number of breaths per -
minute goes up to increase ↳ endothermic absorb sunlight to change lightenergy
intoChemicalenergy
Of levels in the blood
. reaction d
I takes in energy at stard
ADAPTATIONS for photosynthesis from surroundings)
- glucose fructose sucrose ·
(leaf cross-section) >
-
henosugar
wasy
- cutide Chlorophyl
word
L
equaticarbon
on
--upper a
wate
epidermis
>
-
glucose +
Oxygen
Light