Unit 19: Practical Chemical Analysis
B: Investigate spectroscopic techniques to identify compounds and determine concentrations.
The concentration of copper(II) ions in a solution from a sample of brass, by using colorimeter
Beer’s law states that the intensity of the colour is directly proportional to the concentration of
coloured particles in the solution. This means that solutions which have a high concentration of
metal ions, will have a more intense the colour and therefore the absorbance will be greater. Beer’s
law is used to calculate the unknown concentration of a metal ion in a solution using the absorbance
which is measured through colorimetry. This can be expressed as the equation A=Ɛbc, where A is
absorbance, Ɛ is molar absorptivity, b is the length of the light path and c is concentration. When
determining the concentration of an unknown solution, a graph of absorbance against concentration.
A straight line which passes through the point (0,0) can be added to the graph which can then be
used to determine the unknown concentration of a solution.
Equipment:
Brass solution
Copper (II) nitrate to make up 10cm3 of a stock solution of 0.4 mol dm-3
Distilled water
Balance
Six cuvettes
10ml syringe
Four 5ml syringes
Six plastic pipettes
Colorimeter set to wavelength 680nM
0.4M copper (II) nitrate stock solution
Preparation of brass sample solution:
1. Add brass pieces (1g) to a small weighing dish and determine the exact mass. Place in a 50ml
beaker.
2. Place the beaker in a fume cupboard and dispense 6ml of 15.8M nitric acid into the beaker
(cover beaker with a watch glass).
3. Place the beaker on a hot plate set on low. The brass should be completely dissolved within
10-20 minutes. Once the brass has dissolved, carefully remove the beaker from the hot plate
and let it cool.
4. With the beaker still in the fume cupboard, use a graduated cylinder to carefully add 30ml of
distilled water to the beaker and stir the solution with a stirring rod. The beaker can now be
removed from the fume cupboard.
5. Transfer the solution in the beaker to a 100 ml volumetric flask and rinse the beaker with a
small amount of distilled water. Transfer the rinse water to the flask. Repeat this washing two
more times. Fill the flask to the mark with distilled water. Cap and mix well.
Preparation of Cu2+ standard solution:
, Emilia Hawkins
1. Calculate the volumes of 0.40M copper (II) nitrate stock solution and water required to
prepare 4.0cm3 of the following standard solutions for your calibration curve: 0.05M, 0.10M,
0.20M, 0.30M, 0.40M.
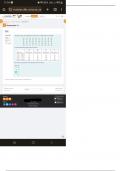
Concentration (M) CuSO4 H2O
0.05 1.25 8.75
0.10 2.5 7.5
0.20 5 5
0.30 7.5 2.5
0.40 10 0
2. Using the answers to my calculation above, prepare 4.0cm 3 of each standard solution in a
small test tube and transfer them to cuvettes. Make sure that each solution is well mixed and
use clean pipettes.
3. Prepare a ‘blank’ by filling a cuvette with distilled water. Fill another cuvette with some of the
brass solution.
Calibration curve for Cu2+ solutions
1. Set the colorimeter to wavelength 680nM, using the adjustment dial on the side.
2. Reference the colorimeter by placing the cuvette containing distilled water into the machine
and pressing ‘R’.
3. Take an absorbance reading of the 0.05M copper (II) nitrate solution by placing the cuvette in
the colorimeter and pressing ‘T’.
4. Re-run the ‘blank’ as in (2) and repeat (3) for 0.10M, 0.20M, 0.30M, 0.40M copper (II) nitrate
and the brass solution. Make sure you blank the colorimeter reading before taking each
sample reading.
Concentration (M) Absorbance
0.05 0.23
0.1 0.41
0.2 0.55
0.3 0.77
0.4 1.10
Absorbancy of CuSO4 + H2O solutions
1.2
1
0.8
Absorbance
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45
Concentration (M)