Flexible Budgets, Direct-Cost Variances
A variance is the difference between actual results and
expected performance. The expected performance is also
called budgeted performance, which is a point of reference
for making comparisons.
Management by exception is a practice whereby managers
focus more closely on areas that are not operating as
expected and less closely on areas that are.
Understand the reason for the decrease (better operator
training or changes in manufacturing methods) so these
practices can be continued and implemented by other
divisions
Evaluating performance to motivate manager
Variances help to make more informed predictions
about the future and thereby improve the quality of the
A flexible budget calculates budgeted revenues and
five-step decision making process
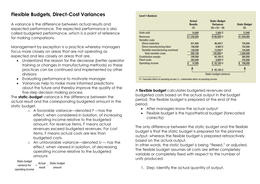
budgeted costs based on the actual output in the budget
The static-budget variance is the difference between the
period. The flexible budget is prepared at the end of the
actual result and the corresponding budgeted amount in the
period.
static budget.
After managers know the actual output
o A favorable variance—denoted F —has the
Flexible budget is the hypothetical budget (forecasted
effect, when considered in isolation, of increasing
correctly)
operating income relative to the budgeted
amount. For revenue items, F means actual
The only difference between the static budget and the flexible
revenues exceed budgeted revenues. For cost
budget is that the static budget is prepared for the planned
items, F means actual costs are less than
output, whereas the flexible budget is prepared retroactively
budgeted costs.
based on the actual output.
o An unfavorable variance—denoted U — has the
In other words, the static budget is being “flexed,” or adjusted.
effect, when viewed in isolation, of decreasing
The flexible budget assumes all costs are either completely
operating income relative to the budgeted
variable or completely fixed with respect to the number of
amount
units produced.
1. Step: Identify the actual quantity of output.
A variance is the difference between actual results and
expected performance. The expected performance is also
called budgeted performance, which is a point of reference
for making comparisons.
Management by exception is a practice whereby managers
focus more closely on areas that are not operating as
expected and less closely on areas that are.
Understand the reason for the decrease (better operator
training or changes in manufacturing methods) so these
practices can be continued and implemented by other
divisions
Evaluating performance to motivate manager
Variances help to make more informed predictions
about the future and thereby improve the quality of the
A flexible budget calculates budgeted revenues and
five-step decision making process
budgeted costs based on the actual output in the budget
The static-budget variance is the difference between the
period. The flexible budget is prepared at the end of the
actual result and the corresponding budgeted amount in the
period.
static budget.
After managers know the actual output
o A favorable variance—denoted F —has the
Flexible budget is the hypothetical budget (forecasted
effect, when considered in isolation, of increasing
correctly)
operating income relative to the budgeted
amount. For revenue items, F means actual
The only difference between the static budget and the flexible
revenues exceed budgeted revenues. For cost
budget is that the static budget is prepared for the planned
items, F means actual costs are less than
output, whereas the flexible budget is prepared retroactively
budgeted costs.
based on the actual output.
o An unfavorable variance—denoted U — has the
In other words, the static budget is being “flexed,” or adjusted.
effect, when viewed in isolation, of decreasing
The flexible budget assumes all costs are either completely
operating income relative to the budgeted
variable or completely fixed with respect to the number of
amount
units produced.
1. Step: Identify the actual quantity of output.