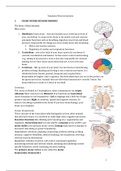
(1.1) Lagrange interpolating polynomial:
P(x)=f(0.1)L0(x)+f(0.2)L1(x)+f(0.3)L2(x)+f(0.4)L3(x)
P(x)=[(−0.29005)(x−0.2)(x−0.3)(x−0.4)]/0.027+[(−0.56079)(x−0.1)(x−0.3)(x−0.4)]/0.027+[(−0.81402)(x−0.1
)(x−0.2)(x−0.4)]/0.027+[(−1.05263)(x−0.1)(x−0.2)(x−0.3)]/0.027
P(x)=16.6667x3−18.3333x2+0.0833x−0.175
To approximate the value of f(0.18), we substitute x=0.18 into the polynomial:
P(0.18)=16.6667(0.18)3−18.3333(0.18)2+0.0833(0.18)−0.175
P(0.18)≈−0.57024
Therefore, the approximation of f(0.18) using the Lagrange interpolating polynomial of degree three is
approximately -0.57024
For (1.2)
To find the error bound, we need to calculate the maximum value of the third derivative of f(x) within
the interval [0.1,0.4].
f‴(x)=−2cos(x)+6x−2x2sin(x)
We evaluate f‴(x) at the endpoints and critical points within the interval to find the maximum value:
f‴(0.1)≈−2cos(0.1)+6(0.1)−2(0.1)2sin(0.1)≈5.95312
f‴(0.4)≈−2cos(0.4)+6(0.4)−2(0.4)2sin(0.4)≈7.567
The maximum value of f‴(x) within the interval [0.1,0.4] is 7.567.
Now, let's calculate the error bound using the formula:
Eb=max|f‴(x)|×|(x−x0)(x−x1)(x−x2)(x−x3)|4!×n
Eb=0.001023
Given that the function generating the data is f ( x ) = x 2 cos ( x ) − 3 x , we can evaluate the true
function value at x = 0.18 and compare it with the approximation obtained earlier.
Calculating the actual value of f ( 0.18 ) : f ( 0.18 ) = ( 0.18 ) 2 cos ( 0.18 ) − 3 × 0.18
f ( 0.18 ) ≈ − 0.58002
Now, we can calculate the actual error:
, APM2613 03
E_a = | f ( 0.18 ) − P ( 0.18 ) | E_a = | − 0.58002 − ( − 0.57024 ) |
E_a ≈ 0.00978
Therefore, the actual error in the approximation obtained using the Lagrange interpolating polynomial is
approximately 0.00978 .
(i) Therefore, the approximation of f ( 0.18 ) using the Lagrange interpolating polynomial of
degree three is approximately − 0.57024 .
(ii) Therefore, the error bound for the Lagrange polynomial is 0.001023 .
(iii) Therefore, the actual error in the approximation obtained using the Lagrange interpolating
polynomial is approximately 0.00978 .