Procurement Management
Module 1: Procurement management
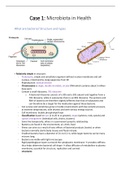
The Purchasing Model
Procurement
Purchasing
Procurement vs. Purchasing
!! Terms “Procurement” & “Purchasing” often used interchangeably..but they are different !!
procurement: operational aspect of buying something)
more strategic
“Purchase order”
Supplier Goods 2
Customer
Invoice
SAP SAP
Money $ 3 1
“Sales order”
Procurement Mgt is about ….
1
,The 5R’s of Procurement
• The 5 Rights of Procurement .. - In the Right Place
- At the Right Time.
- In the Right Quantity, • Extensions to 6R, 7R, ….
- At the Right Quality - To Acquire the right material
- At the Right Price - From the Right Supplier
Business Context
• Which Business Context are we in ?
- Which Economic Sector ?
- Which Type of Business : B2B, B2C, .. ?
- Which Company size ?
- What is the Company structure ?
4 Economic Sectors
Primary sector: focuses on cost
Service Industries: focus on adding value
(B2B & B2C doesn’t make much difference from a
procurement POV)
Porter Value Chain model
2
,• A typical company structure..including supporting services
• Supporting activities are working for all departments/primary activites
What’s Procurement’s place in the Value Chain?
• Although Procurement department is typically as ‘supporting service’, it is of strategic
importance
• A well-organized procurement department will be the source of intelligence to know:
- Who you are sourcing and procuring goods/services from?
- How those goods/services are being produced or delivered?
- Why you are procuring from those particular suppliers?
- When to eliminate defective/non-compliant suppliers?
• Purchasing is seen as an area for adding value, not simply reducing costs.
• Reducing price and availability risks in the supply chain
• Awareness that active supplier involvement can increase efficiency and
effectiveness.
• A developing recognition that concern with strategic costs of supply and total cost of
ownership (TCO), rather than short-term price, is important.
TCO= doesn’t only look at initial cost, BUT full cost
Exercise: You are buying a car with a budget of 10.000 $
electric car 59.000 $
Or
Diesel/Gas car 25.000 $
answer: If you only look at the initial price, you will choose for diesel, but if maintenance will
cost you more in the long run.
Procurement Roles/Functions
Function: full time job
Role: temporary thing that you have to execute
• Variations depending on company size
3
, Procurement role : isolated ?
• Not an isolated role/function
• Interaction with many colleagues/departments INSIDE the company
• Interaction with suppliers OUTSIDE the company
Interaction with others
• A procurement role/functions is never working at its own
• Does she/he knows al the details of the goods to be purchased ?
• Typically working for an ”Internal Customer”
- Defining the “needs” & the details (see Specifications”)
• For significant purchases, a DMU (Decision Making Unit) is composed
DMU (Decision Making Unit)
• What ?
- team of individuals who participate in a buyer decision process.
- relates to business or organizational buying decisions.
• Why ?
- Minimalise the risk by involving as many people as possible in the
decision making process.
• Who ?
Typical Roles:
The future of procurement mgt
4
Module 1: Procurement management
The Purchasing Model
Procurement
Purchasing
Procurement vs. Purchasing
!! Terms “Procurement” & “Purchasing” often used interchangeably..but they are different !!
procurement: operational aspect of buying something)
more strategic
“Purchase order”
Supplier Goods 2
Customer
Invoice
SAP SAP
Money $ 3 1
“Sales order”
Procurement Mgt is about ….
1
,The 5R’s of Procurement
• The 5 Rights of Procurement .. - In the Right Place
- At the Right Time.
- In the Right Quantity, • Extensions to 6R, 7R, ….
- At the Right Quality - To Acquire the right material
- At the Right Price - From the Right Supplier
Business Context
• Which Business Context are we in ?
- Which Economic Sector ?
- Which Type of Business : B2B, B2C, .. ?
- Which Company size ?
- What is the Company structure ?
4 Economic Sectors
Primary sector: focuses on cost
Service Industries: focus on adding value
(B2B & B2C doesn’t make much difference from a
procurement POV)
Porter Value Chain model
2
,• A typical company structure..including supporting services
• Supporting activities are working for all departments/primary activites
What’s Procurement’s place in the Value Chain?
• Although Procurement department is typically as ‘supporting service’, it is of strategic
importance
• A well-organized procurement department will be the source of intelligence to know:
- Who you are sourcing and procuring goods/services from?
- How those goods/services are being produced or delivered?
- Why you are procuring from those particular suppliers?
- When to eliminate defective/non-compliant suppliers?
• Purchasing is seen as an area for adding value, not simply reducing costs.
• Reducing price and availability risks in the supply chain
• Awareness that active supplier involvement can increase efficiency and
effectiveness.
• A developing recognition that concern with strategic costs of supply and total cost of
ownership (TCO), rather than short-term price, is important.
TCO= doesn’t only look at initial cost, BUT full cost
Exercise: You are buying a car with a budget of 10.000 $
electric car 59.000 $
Or
Diesel/Gas car 25.000 $
answer: If you only look at the initial price, you will choose for diesel, but if maintenance will
cost you more in the long run.
Procurement Roles/Functions
Function: full time job
Role: temporary thing that you have to execute
• Variations depending on company size
3
, Procurement role : isolated ?
• Not an isolated role/function
• Interaction with many colleagues/departments INSIDE the company
• Interaction with suppliers OUTSIDE the company
Interaction with others
• A procurement role/functions is never working at its own
• Does she/he knows al the details of the goods to be purchased ?
• Typically working for an ”Internal Customer”
- Defining the “needs” & the details (see Specifications”)
• For significant purchases, a DMU (Decision Making Unit) is composed
DMU (Decision Making Unit)
• What ?
- team of individuals who participate in a buyer decision process.
- relates to business or organizational buying decisions.
• Why ?
- Minimalise the risk by involving as many people as possible in the
decision making process.
• Who ?
Typical Roles:
The future of procurement mgt
4