The Genome
The DNA is contained
in structures called
chromosomes.
The genetic material in the
nucleus of a cell is made of a
chemical called DNA
(deoxynucleotide acid).
A gene is a small
section of DNA in a
chromosome.
Genes
Each gene codes for a particular sequence of
amino acids, to make a specific protein (it tells combined to
cells how to make them), which codes for a make protein
characteristic, e.g. eye colour.
Different versions of genes are called alleles.
You have a pair of genes – one from each chromosome – to control each characteristic.
The genome of an organism is its entire genetic material.
Diploid vs Haploid
Human diploid cells: those with 46 chromosomes (23 pairs)
Human haploid gametes: those with 23 chromosomes (sperm and ovum)
, Human Genome Project
The whole human genome has now been studied.
AIMS OF THE HGP - Work out order/sequence of all three billion base pairs
in the human genome
- Identify all the genes
- Develop faster methods for sequencing DNA
WHAT THEY MUST NOW DO - Work out what the codes control
- Which parts of code are genes
- Which parts of code is ‘junk’ (e.g. non-coding)
USES IN THE FUTURE - Doctors can search for genes linked to different types
of disorders
- Help scientists to understand the cause of inherited
disorders and how to treat them
- Investigate how humans have changed over time, and
how ancient ancestors migrated across the globe
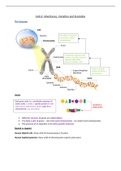
The Structure of DNA
DNA is a long molecule of
two strands twisted together
to make a double helix.
The four different types of
organic
nucleobases.Complementa
ry base pairs is the idea of
the attraction connecting
bases together on opposite
strands: C-G and A-
T.Genetic code is the
sequence of these base
pairs.
phosphate DNA is a polymer made up of repeating
nucleotide (monomers) units
base
A,C,G,T
deoxyribose sugar
The nucleotides are connected together to make Nucleotides are made up of a
one long chain called a sugar-phosphate backbone. phosphate + a sugar + an organic base
phosphate
base
A,C,G,U
ribose sugar