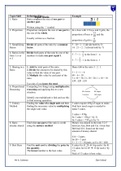
Topic/Skill Definition/Tips
Topic: Ratio Example
1. Ratio Ratio compares the size of one part to
another part.
Written using the ‘:’ symbol.
2. Proportion Proportion compares the size of one part to In a class with 13 boys and 9 girls, the
the size of the whole. 13
proportion of boys is and the
22
Usually written as a fraction. 9
proportion of girls is
22
3. Simplifying Divide all parts of the ratio by a common 5 : 10 = 1 : 2 (divide both by 5)
Ratios factor. 14 : 21 = 2 : 3 (divide both by 7)
4. Ratios in the Divide both parts of the ratio by one of the 7
5:7=1: in the form 1 : n
form 1 :n or numbers to make one part equal 1. 5
n :1 5
5:7= : 1 in the form n : 1
7
5. Sharing in a 1. Add the total parts of the ratio. Share £60 in the ratio 3 : 2 : 1.
Ratio 2. Divide the amount to be shared by this
value to find the value of one part. 3+2+1=6
3. Multiply this value by each part of the 60 ÷ 6 = 10
ratio. 3 x 10 = 30, 2 x 10 = 20, 1 x 10 = 10
£30 : £20 : £10
Use only if you know the total.
6. Proportional Comparing two things using multiplicative
Reasoning reasoning and applying this to a new
situation.
Identify one multiplicative link and use this
to find missing quantities.
7. Unitary Finding the value of a single unit and then 3 cakes require 450g of sugar to make.
Method finding the necessary value by multiplying Find how much sugar is needed to
the single unit value. make 5 cakes.
3 cakes = 450g
So 1 cake = 150g (÷ by 3)
So 5 cakes = 750 g (x by 5)
8. Ratio Find what one part of the ratio is worth Money was shared in the ratio 3:2:5
already shared using the unitary method. between Ann, Bob and Cat. Given that
Bob had £16, found out the total
amount of money shared.
£16 = 2 parts
So £8 = 1 part
3 + 2 + 5 = 10 parts, so 8 x 10 = £80
9. Best Buys Find the unit cost by dividing the price by 8 cakes for £1.28 16p each (÷by 8)
the quantity. 13 cakes for £2.05 15.8p each (÷by
The lowest number is the best value. 13)
Pack of 13 cakes is best value.
Mr A. Coleman Glyn School
Topic: Ratio Example
1. Ratio Ratio compares the size of one part to
another part.
Written using the ‘:’ symbol.
2. Proportion Proportion compares the size of one part to In a class with 13 boys and 9 girls, the
the size of the whole. 13
proportion of boys is and the
22
Usually written as a fraction. 9
proportion of girls is
22
3. Simplifying Divide all parts of the ratio by a common 5 : 10 = 1 : 2 (divide both by 5)
Ratios factor. 14 : 21 = 2 : 3 (divide both by 7)
4. Ratios in the Divide both parts of the ratio by one of the 7
5:7=1: in the form 1 : n
form 1 :n or numbers to make one part equal 1. 5
n :1 5
5:7= : 1 in the form n : 1
7
5. Sharing in a 1. Add the total parts of the ratio. Share £60 in the ratio 3 : 2 : 1.
Ratio 2. Divide the amount to be shared by this
value to find the value of one part. 3+2+1=6
3. Multiply this value by each part of the 60 ÷ 6 = 10
ratio. 3 x 10 = 30, 2 x 10 = 20, 1 x 10 = 10
£30 : £20 : £10
Use only if you know the total.
6. Proportional Comparing two things using multiplicative
Reasoning reasoning and applying this to a new
situation.
Identify one multiplicative link and use this
to find missing quantities.
7. Unitary Finding the value of a single unit and then 3 cakes require 450g of sugar to make.
Method finding the necessary value by multiplying Find how much sugar is needed to
the single unit value. make 5 cakes.
3 cakes = 450g
So 1 cake = 150g (÷ by 3)
So 5 cakes = 750 g (x by 5)
8. Ratio Find what one part of the ratio is worth Money was shared in the ratio 3:2:5
already shared using the unitary method. between Ann, Bob and Cat. Given that
Bob had £16, found out the total
amount of money shared.
£16 = 2 parts
So £8 = 1 part
3 + 2 + 5 = 10 parts, so 8 x 10 = £80
9. Best Buys Find the unit cost by dividing the price by 8 cakes for £1.28 16p each (÷by 8)
the quantity. 13 cakes for £2.05 15.8p each (÷by
The lowest number is the best value. 13)
Pack of 13 cakes is best value.
Mr A. Coleman Glyn School