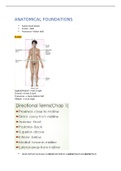
ANATOMICAL FOUNDATIONS
Supine (back down)
Crania = skull
Postcrania = below skull
PLANES
Sagittal(Medial) → left & right
Coronal → front & back
Transverse → top & bottom half
Oblique → at an angle
Hand and foot top known as dorsal and bottom is palmar(hand) and plantar(foot)
, Superficial → closer to surface
Deep → further away from surface
o Muscles are superficial vs bone
Facia is a network of tissue that groups other tissues together
o Protects muscles and helps with function
SURFACE LAYERS OF BODY
1. Skin or epidermis
2. Superficial fascia
Layer of loose fatty connective tissue underlying the dermis & binding it to parts beneath
Sensory nerves for skin run through it
Contains veins, arteries & lymphatic vessels
Varies in thickness across body
3. Deep fascia
Little network of fascia between muscles
o When someone damages the muscle, often damages fascia as well
Layer of dense fibrous tissue which surrounds individual muscles & divide groups of muscles
into fascial compartments
Attaches to bone
Intermuscular septa - runs between muscles
At wrist & ankle deep fascia is found & forms retinacula → thick fibrous band around groups
of tendons that holds them in place
→ function to stabilize tendon
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Supply oxygen & nutrients
o Oxygenated blood = arteries
o Deoxygenated blood = veins
Lungs get deoxygenated blood from veins
Supine (back down)
Crania = skull
Postcrania = below skull
PLANES
Sagittal(Medial) → left & right
Coronal → front & back
Transverse → top & bottom half
Oblique → at an angle
Hand and foot top known as dorsal and bottom is palmar(hand) and plantar(foot)
, Superficial → closer to surface
Deep → further away from surface
o Muscles are superficial vs bone
Facia is a network of tissue that groups other tissues together
o Protects muscles and helps with function
SURFACE LAYERS OF BODY
1. Skin or epidermis
2. Superficial fascia
Layer of loose fatty connective tissue underlying the dermis & binding it to parts beneath
Sensory nerves for skin run through it
Contains veins, arteries & lymphatic vessels
Varies in thickness across body
3. Deep fascia
Little network of fascia between muscles
o When someone damages the muscle, often damages fascia as well
Layer of dense fibrous tissue which surrounds individual muscles & divide groups of muscles
into fascial compartments
Attaches to bone
Intermuscular septa - runs between muscles
At wrist & ankle deep fascia is found & forms retinacula → thick fibrous band around groups
of tendons that holds them in place
→ function to stabilize tendon
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Supply oxygen & nutrients
o Oxygenated blood = arteries
o Deoxygenated blood = veins
Lungs get deoxygenated blood from veins