AXIAL SKELETON
Include cranial(skull) , vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, manubrium, sternum and ribs
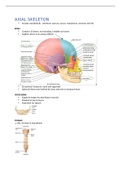
SKULL
Contains 22 bones, not including 3 middle ear bones
Sagittal suture (runs along midline)
2 x parietal, temporal, nasal and zygomatic
Sphenoid bone seen behind the eyes and next to temporal bone
HYOID BONE
Supports tongue by attaching to muscles
Situated at top of larynx
Important for speech
THORAX
→ ribs, sternum & manubrium
, Sternum is made up of manubrium & body
Ribs attach to sternum with cartilaginous joint
Suprasternal notch → entry of some vessels
Ribs fit into articular facets of the vertebrae at the back
12 ribs per side
VERTEBRAE, SACRUM & COCCYX
Cervical (7)
o Atlas (top)
o Axis (second)
Atlas rotates on axis
o 5 other cervical
→ woman who carry large containers of water on their head have a higher chance
of neck injury
Thoracic (12) → attachment to 12 ribs via cartilaginous joints
Lumbar (5)
o Most injury found in lumbar because it carries most of the weight
Sacral (fused 5)
o In non-humans they are loose
Coccyx (tail bone) → found at end
CERVICAL VERTEBRAE
ATLAS Normal
AXIS
, THORACIC
The spinous process are longer in thoracic
o As you move down it gets longer & wider
LUMBAR
Largest & strongest of all vertebrae → because it carries the most weight
SACRUM
5 Fused bones (in adults)
Coccyx → 4 fused bones
APPENDICULAR SKELETON
Primary function movement
Consists of upper and lower limbs
In humans there is a big difference between upper and lower limbs
o Whereas, other animals limbs look very similar
Lack of hair on skin improves our heat dissipation (thermal regulation)
Having free limbs allow us to carry and transport food better and the technological
advancement
Longer legs = increased stride (cover greater distances)
o Walking uses minimal calories and water lose
UPPER LIMB
Our most NB sensory systems are sight and touch → large full-colour vision and free hands
Shoulder joint → very open, majority of the joint made up of muscle
Very easy to dislocate
PECTORAL (SHOULDER) GIRDLE
Clavicle (collar bone)
o s-shaped
o Medial → sternal end articulates with manubrium of sternum
o Lateral → acromial end articulates with acromion of scapula
o Superior side smoother then inferior end due to more muscle attachments on
inferior end
Include cranial(skull) , vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, manubrium, sternum and ribs
SKULL
Contains 22 bones, not including 3 middle ear bones
Sagittal suture (runs along midline)
2 x parietal, temporal, nasal and zygomatic
Sphenoid bone seen behind the eyes and next to temporal bone
HYOID BONE
Supports tongue by attaching to muscles
Situated at top of larynx
Important for speech
THORAX
→ ribs, sternum & manubrium
, Sternum is made up of manubrium & body
Ribs attach to sternum with cartilaginous joint
Suprasternal notch → entry of some vessels
Ribs fit into articular facets of the vertebrae at the back
12 ribs per side
VERTEBRAE, SACRUM & COCCYX
Cervical (7)
o Atlas (top)
o Axis (second)
Atlas rotates on axis
o 5 other cervical
→ woman who carry large containers of water on their head have a higher chance
of neck injury
Thoracic (12) → attachment to 12 ribs via cartilaginous joints
Lumbar (5)
o Most injury found in lumbar because it carries most of the weight
Sacral (fused 5)
o In non-humans they are loose
Coccyx (tail bone) → found at end
CERVICAL VERTEBRAE
ATLAS Normal
AXIS
, THORACIC
The spinous process are longer in thoracic
o As you move down it gets longer & wider
LUMBAR
Largest & strongest of all vertebrae → because it carries the most weight
SACRUM
5 Fused bones (in adults)
Coccyx → 4 fused bones
APPENDICULAR SKELETON
Primary function movement
Consists of upper and lower limbs
In humans there is a big difference between upper and lower limbs
o Whereas, other animals limbs look very similar
Lack of hair on skin improves our heat dissipation (thermal regulation)
Having free limbs allow us to carry and transport food better and the technological
advancement
Longer legs = increased stride (cover greater distances)
o Walking uses minimal calories and water lose
UPPER LIMB
Our most NB sensory systems are sight and touch → large full-colour vision and free hands
Shoulder joint → very open, majority of the joint made up of muscle
Very easy to dislocate
PECTORAL (SHOULDER) GIRDLE
Clavicle (collar bone)
o s-shaped
o Medial → sternal end articulates with manubrium of sternum
o Lateral → acromial end articulates with acromion of scapula
o Superior side smoother then inferior end due to more muscle attachments on
inferior end