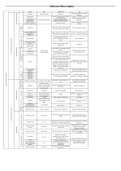
NEUROBIOLOGY
,Lecture 1 – Nervous system: Structure + Function + Types of Nerve
cells
Nervous System:
The nerves of the nervous system branch from the brain + spinal cord to innervate
every part of the body
Neurons/Nerve cells
- Functional cell responsible for nervous system signalling
- Cells specialised for communication
How do neurons function?
By sending either:
- Long distance electrical signals → electrical impulses OR action potentials
from part of body to another
- Short distance chemical signals
Higher order processing is done in brain + ganglia (Process nerve impulses as
groups of neurons organised in the brain or simpler clusters)
CNS (Central Nervous System) – neurons that carry out integration
PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) – neurons that carry information into and out of
CNS
,Neuron Structure
1. Cell Body → main body, integration centre, organelles including nucleus
(DNA) + mitochondria
2. Dendrites → cytoplasmic branched extensions of cell body, receive
information from receptors or other neurons
3. Axon → slender tube of cell membrane, small amount of cytoplasm,
enclosed in a myelin sheath, is specialised to transmit action potential away
from cell body
Axons are longer than dendrites
4. Axon Hillock → cone-shaped area of cell body, area where signals that
travel down axon are generated
5. Axon terminal → extensions of axon branches
6. Presynaptic cells + post synaptic cells → synapse terminal, 100 000
synapses with highly branched dendrites
Presynaptic cell → transmitting neuron
Postsynaptic cell → receiving neuron, muscle, or gland cell, receive signal
from synaptic terminal of presynaptic cell
7. Synaptic terminal → part of axon branch that forms specialised junction
8. Synapse → branched end of axon/junction where a neuron communicates
with another cell across a narrow gap via a neurotransmitter of an electrical
coupling
9. Neurotransmitter → a chemical messenger/molecule released form the
synaptic terminal of a neuron at a chemical synapse, diffuses across the
synaptic cleft and binds to the postsynaptic cell, triggering a response
, Neuron’s function in receiving and transmitting information.
Cell body houses the organelles + nucleus. The cell body is studded with highly
branched extensions called Dendrites (short) which receive signals.
Has a single Axon (long) which transmits signals by using pulses of electrical
current to transmit information.
Axon Hillock is the cone-shaped base of an Axon, site where signals are generated
before going down Axon.
At the end of an Axon, the Axon branches. Each branched end transmits
information to another cell at a junction called a Synapse. The part of each Axon
branch that forms this specialized junction is a Synaptic Terminal. Chemical
messengers called Neurotransmitters pass information from transmitting neuron
cell to target cell.
A bundle of neurons = Nerves
,Lecture 1 – Nervous system: Structure + Function + Types of Nerve
cells
Nervous System:
The nerves of the nervous system branch from the brain + spinal cord to innervate
every part of the body
Neurons/Nerve cells
- Functional cell responsible for nervous system signalling
- Cells specialised for communication
How do neurons function?
By sending either:
- Long distance electrical signals → electrical impulses OR action potentials
from part of body to another
- Short distance chemical signals
Higher order processing is done in brain + ganglia (Process nerve impulses as
groups of neurons organised in the brain or simpler clusters)
CNS (Central Nervous System) – neurons that carry out integration
PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) – neurons that carry information into and out of
CNS
,Neuron Structure
1. Cell Body → main body, integration centre, organelles including nucleus
(DNA) + mitochondria
2. Dendrites → cytoplasmic branched extensions of cell body, receive
information from receptors or other neurons
3. Axon → slender tube of cell membrane, small amount of cytoplasm,
enclosed in a myelin sheath, is specialised to transmit action potential away
from cell body
Axons are longer than dendrites
4. Axon Hillock → cone-shaped area of cell body, area where signals that
travel down axon are generated
5. Axon terminal → extensions of axon branches
6. Presynaptic cells + post synaptic cells → synapse terminal, 100 000
synapses with highly branched dendrites
Presynaptic cell → transmitting neuron
Postsynaptic cell → receiving neuron, muscle, or gland cell, receive signal
from synaptic terminal of presynaptic cell
7. Synaptic terminal → part of axon branch that forms specialised junction
8. Synapse → branched end of axon/junction where a neuron communicates
with another cell across a narrow gap via a neurotransmitter of an electrical
coupling
9. Neurotransmitter → a chemical messenger/molecule released form the
synaptic terminal of a neuron at a chemical synapse, diffuses across the
synaptic cleft and binds to the postsynaptic cell, triggering a response
, Neuron’s function in receiving and transmitting information.
Cell body houses the organelles + nucleus. The cell body is studded with highly
branched extensions called Dendrites (short) which receive signals.
Has a single Axon (long) which transmits signals by using pulses of electrical
current to transmit information.
Axon Hillock is the cone-shaped base of an Axon, site where signals are generated
before going down Axon.
At the end of an Axon, the Axon branches. Each branched end transmits
information to another cell at a junction called a Synapse. The part of each Axon
branch that forms this specialized junction is a Synaptic Terminal. Chemical
messengers called Neurotransmitters pass information from transmitting neuron
cell to target cell.
A bundle of neurons = Nerves