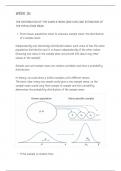
COSTS A BREAK -
EVEN
break -
even
analysis :
a method for finding out the minimum
level of sales necessary for a firm to
cover all of its costs with revenue
↳ at the break -
even point ,
the revenue obtained from the
all the costs out in making and
sale of products equals paid
selling them
↳ when costs are greater than revenue the firm makes a loss
↳ when costs are less than revenue the firm will make a profit
↳ break even
when costs equal revenue the firm will
fixed cost which does as the amount of products
cost a not
change
:
I called overheads )
produced or sold
changes also
↳
examples :
costs are constant at
her rent
EE -
all levels of production
we
rates
be insurance
the salaries output
↳ fixed costs
per
unit of output will decrease as
production
increases (vice versa ) as the same amount of fixed costs can
be shared out over a
larger number of
products
variable cost which changes amount of
cost a as the goods
:
produced or sold
changes
↳ direct costs
examples
: :
Lee materials used in production
ÉÉ iii. ! :
directly involved
in
i.
producing
her
wages ( piece rate ) a product
output
↳ variable costs per unit of production doesn't change
, r
total costs
= total fixed costs + total variable costs
6
Tc T
=Y¥i÷p
""
average
-
É an ,
output
revenue the money that comes in from
selling the goods / services
:
revenue
'
when nothing is
sold , no revenue is
a-
made but as sales
increase , revenue also
increases proportionally
output
break total fixed costs
even point
-
=
contribution unit )
lper
↳
variable cost /per unit )
contribution selling price
-
=
be contribution refers to the amount of
after all variable costs
money remaining
have been subtracted from sales revenue
↳ in units
break even (f) BEP ✗
selling price
point
-
=
↳ BE level of output
margin of
safety actual output -
=
EVEN
break -
even
analysis :
a method for finding out the minimum
level of sales necessary for a firm to
cover all of its costs with revenue
↳ at the break -
even point ,
the revenue obtained from the
all the costs out in making and
sale of products equals paid
selling them
↳ when costs are greater than revenue the firm makes a loss
↳ when costs are less than revenue the firm will make a profit
↳ break even
when costs equal revenue the firm will
fixed cost which does as the amount of products
cost a not
change
:
I called overheads )
produced or sold
changes also
↳
examples :
costs are constant at
her rent
EE -
all levels of production
we
rates
be insurance
the salaries output
↳ fixed costs
per
unit of output will decrease as
production
increases (vice versa ) as the same amount of fixed costs can
be shared out over a
larger number of
products
variable cost which changes amount of
cost a as the goods
:
produced or sold
changes
↳ direct costs
examples
: :
Lee materials used in production
ÉÉ iii. ! :
directly involved
in
i.
producing
her
wages ( piece rate ) a product
output
↳ variable costs per unit of production doesn't change
, r
total costs
= total fixed costs + total variable costs
6
Tc T
=Y¥i÷p
""
average
-
É an ,
output
revenue the money that comes in from
selling the goods / services
:
revenue
'
when nothing is
sold , no revenue is
a-
made but as sales
increase , revenue also
increases proportionally
output
break total fixed costs
even point
-
=
contribution unit )
lper
↳
variable cost /per unit )
contribution selling price
-
=
be contribution refers to the amount of
after all variable costs
money remaining
have been subtracted from sales revenue
↳ in units
break even (f) BEP ✗
selling price
point
-
=
↳ BE level of output
margin of
safety actual output -
=