Electric cells as energy systems: Topic 11 page 145-149
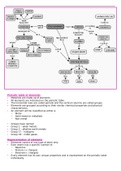
A cell is a system that supplies energy. A cell produces electricity. It converts chemical energy into
electrical energy. A chemical reaction in the cell releases electrons that flow through a circuit.
Input Process Output
A chemical reaction occurred between the beakers. This made electrons move from the zinc plate to
the copper plate. Showing a reading on the voltmeter. The metal plates are called electrodes. The
solution around the plates is called an electrolyte – this allows electrons to flow through it.
Dry cell – cannot be recharged. Wet cell – can be recharged. Eg. Car and cell phone batteries
Batteries: Two or more cells. Store energy as chemical energy.
Voltage: Cells have their voltage marked on them. Voltage can also be called potential difference. It
is a measure of the amount of potential energy stored in the cell. We measure this in volts. We can
measure this with a voltmeter.
Safety with electricity and the national electricity grid: Topic 14 – Page 175-185
Problems with parallel connections: Adding more parallel branches to a circuit means there is more
current running though the main wire. This means it is easy to overload a circuit by requiring more
current than the circuit can handle. This can cause a fire or a short circuit – this is wires melt and
break. Power lines come into your house and are connected to a fuse box. These fuses prevent too
much electric current from entering a house. A fuse is a safety device that has a thin strip of metal
that melts and breaks if the current exceeds a certain level. Too much current can cause overheating
and fires.
Circuit breaker: Also prevents too high a current from flowing through a wire. Circuit boards will use
circuit breakers instead of fuses.
Earth leakage: Protects the power distribution system. Found in the mains circuit board. Redirects
current into the ground. Current entering a device = current leaving a device. If current flows where
it shouldn’t – it will be redirected down the earth leakage wire.
Three-pin plugs: This is safer than a plug that just has a live wire and a neutral wire. It has a live
wire, a neutral wire and an earth wire. If the metal casing of an appliance (e.g. A kettle) accidentally
becomes electrically charged, the earth wire would be attached to this and would direct the excess
current into the ground which prevents you from being electrocuted.
A cell is a system that supplies energy. A cell produces electricity. It converts chemical energy into
electrical energy. A chemical reaction in the cell releases electrons that flow through a circuit.
Input Process Output
A chemical reaction occurred between the beakers. This made electrons move from the zinc plate to
the copper plate. Showing a reading on the voltmeter. The metal plates are called electrodes. The
solution around the plates is called an electrolyte – this allows electrons to flow through it.
Dry cell – cannot be recharged. Wet cell – can be recharged. Eg. Car and cell phone batteries
Batteries: Two or more cells. Store energy as chemical energy.
Voltage: Cells have their voltage marked on them. Voltage can also be called potential difference. It
is a measure of the amount of potential energy stored in the cell. We measure this in volts. We can
measure this with a voltmeter.
Safety with electricity and the national electricity grid: Topic 14 – Page 175-185
Problems with parallel connections: Adding more parallel branches to a circuit means there is more
current running though the main wire. This means it is easy to overload a circuit by requiring more
current than the circuit can handle. This can cause a fire or a short circuit – this is wires melt and
break. Power lines come into your house and are connected to a fuse box. These fuses prevent too
much electric current from entering a house. A fuse is a safety device that has a thin strip of metal
that melts and breaks if the current exceeds a certain level. Too much current can cause overheating
and fires.
Circuit breaker: Also prevents too high a current from flowing through a wire. Circuit boards will use
circuit breakers instead of fuses.
Earth leakage: Protects the power distribution system. Found in the mains circuit board. Redirects
current into the ground. Current entering a device = current leaving a device. If current flows where
it shouldn’t – it will be redirected down the earth leakage wire.
Three-pin plugs: This is safer than a plug that just has a live wire and a neutral wire. It has a live
wire, a neutral wire and an earth wire. If the metal casing of an appliance (e.g. A kettle) accidentally
becomes electrically charged, the earth wire would be attached to this and would direct the excess
current into the ground which prevents you from being electrocuted.