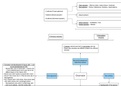
- Telencephalon ? Olfactory lobes, Hippocampus, Cerebrum
- Diencephalon ? Retina, Epithalamus, thalamus, Hypothalamus
- Forebrain (Prosencephalon)
- Midbrain (Mesencephalon) - Mesencephalon
- Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)
- Metencephalon ? Cerebellum, Pons
- Myelencephalon ? Medulla
5 Secondary
3 Primary Vesicles
Vesicles
- 3 primary vesicles give rise to 5 secondary vesicles
- Neural tube develops into different shapes (the different
vesicles)
Neural Development:
Adult Derivatives
= Formation and development of nerve cells ?> set
up and development of CNS
- Neural stem cells in neural tube -> neural cells
-> forms different layers which give rise to the
different layers in the mature CNS
- Neural crest cells migrate as neural tube closes
- Neural Tube (Gives rise to CNS) becomes site of Neurogenesis Overveiw Neurulation
Neurogenesis
- NSC (Neural Stem Cell) niches: Area where stem
cells retain activity over a prolonged period.
- Neurogenesis very active in embryology, and
even up to puberty ? but then seizes and Development of the nervous
, - Lacks cortical grey matter ? has inner grey matter in butterfly shape
- Interface between CNS and PNS
- Has dorsal roots and ventral roots of spinal peripheral nerves
- Spinal ganglion contains groups of [primary sensory] neurons of the PNS that convey info
from the bodies periphery into the CNS.
- Very repetitive and uniform arrangement down the spinal cord
- Has boundary between CNS & PNS
- Layout: Ependymal layer -> Intermediate zone (grey matter) -> Marginal zone (white matter)
- Big difference to brain is it doesn?t have the radial migration that sets up the cortical layers
The Spinal
Cord
Functional
Histology
- Neurones
- Ependyma (Surround to the
ventricle)
- Supporting cells:
- Astrocytes (most
Cell Types CNS
common)
- Oligodendrocytes
- Microglia
General Organisation
Radial migration
Outward migration of immature Periventricular zo
neurons forms cortex with very - Fluid filled ventricle in middle of neural
- Diencephalon ? Retina, Epithalamus, thalamus, Hypothalamus
- Forebrain (Prosencephalon)
- Midbrain (Mesencephalon) - Mesencephalon
- Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)
- Metencephalon ? Cerebellum, Pons
- Myelencephalon ? Medulla
5 Secondary
3 Primary Vesicles
Vesicles
- 3 primary vesicles give rise to 5 secondary vesicles
- Neural tube develops into different shapes (the different
vesicles)
Neural Development:
Adult Derivatives
= Formation and development of nerve cells ?> set
up and development of CNS
- Neural stem cells in neural tube -> neural cells
-> forms different layers which give rise to the
different layers in the mature CNS
- Neural crest cells migrate as neural tube closes
- Neural Tube (Gives rise to CNS) becomes site of Neurogenesis Overveiw Neurulation
Neurogenesis
- NSC (Neural Stem Cell) niches: Area where stem
cells retain activity over a prolonged period.
- Neurogenesis very active in embryology, and
even up to puberty ? but then seizes and Development of the nervous
, - Lacks cortical grey matter ? has inner grey matter in butterfly shape
- Interface between CNS and PNS
- Has dorsal roots and ventral roots of spinal peripheral nerves
- Spinal ganglion contains groups of [primary sensory] neurons of the PNS that convey info
from the bodies periphery into the CNS.
- Very repetitive and uniform arrangement down the spinal cord
- Has boundary between CNS & PNS
- Layout: Ependymal layer -> Intermediate zone (grey matter) -> Marginal zone (white matter)
- Big difference to brain is it doesn?t have the radial migration that sets up the cortical layers
The Spinal
Cord
Functional
Histology
- Neurones
- Ependyma (Surround to the
ventricle)
- Supporting cells:
- Astrocytes (most
Cell Types CNS
common)
- Oligodendrocytes
- Microglia
General Organisation
Radial migration
Outward migration of immature Periventricular zo
neurons forms cortex with very - Fluid filled ventricle in middle of neural